The brain lacks oxygen. Therapy
Oxygen starvation of the brain or hypoxia occurs due to a disruption in the supply of oxygen to its tissues. The brain is the organ with the greatest need for oxygen. A quarter of all inhaled air goes to serving the brain’s need for it, and 4 minutes without it becomes critical for life. Oxygen enters the brain through a complex blood supply system and is then utilized by its cells. Any disturbances in this system lead to oxygen starvation.
, , , ,
ICD-10 code
G93 Other brain lesions
I67.3 Progressive vascular leukoencephalopathy
Epidemiology
Due to the variety of forms of pathological conditions inherent in oxygen starvation, it is difficult to determine its prevalence. Based on the reasons that give rise to it, the number of people who have experienced this condition is very large. But the statistics of oxygen starvation in newborns are more definite and disappointing: fetal hypoxia is observed in 10 cases out of 100.
, , ,
Causes of oxygen starvation of the brain
There are various reasons for the occurrence of oxygen starvation of the brain. These include:
- decrease in oxygen in the environment (when climbing mountains, indoors, in spacesuits or submarines);
- disruption of the respiratory organs (asthma, pneumonia, chest injuries, tumors);
- disruption of blood circulation in the brain (arterial atherosclerosis, thrombosis, embolism);
- impaired oxygen transport (lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin);
- blockade of enzyme systems involved in tissue respiration.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of oxygen starvation is a change in the structure of the vascular walls, disruption of their permeability, which leads to cerebral edema. Depending on the reasons that caused hypoxia, pathogenesis develops according to a different algorithm. So, with exogenous factors, this process begins with arterial hypoxemia - a decrease in the oxygen content in the blood, which entails hypocapnia - a lack of carbon dioxide, which disrupts the biochemical balance in it. The next chain of negative processes is alkalosis - a failure of the acid-base balance in the body. At the same time, blood flow in the brain and coronary arteries is disrupted, and blood pressure drops.
Endogenous causes caused by pathological conditions of the body cause arterial hypoxemia along with hypercapnia (increased carbon dioxide content) and acidosis (increased oxidation products of organic acids). Different types of hypoxia have their own scenarios of pathological changes.
, , , , , ,
Symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain
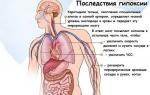
The first signs of oxygen deficiency appear in the excitation of the nervous system: breathing and heartbeat quicken, euphoria sets in, cold sweat appears on the face and limbs, and motor restlessness. Then the condition changes dramatically: lethargy, drowsiness, headache, darkening of the eyes, and depression of consciousness appear. A person becomes dizzy, develops constipation, possible muscle cramps and fainting, and the onset of coma. The most severe degree of coma is deep disturbances of the central nervous system: lack of brain activity, muscle hypotension, respiratory arrest with a beating heart.
Oxygen starvation of the brain in adults
Oxygen starvation of the brain in adults can develop as a result of stroke, when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, hypovolemic shock - a significant decrease in the volume of circulating blood that occurs with large blood loss, uncompensated loss of plasma in burns, peritonitis, pancreatitis, accumulation of a large volume of blood in injuries, dehydration in diarrhea. This condition is characterized by decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, nausea and dizziness, and loss of consciousness.
Oxygen starvation of the brain in children and newborns
Analyzing the various factors causing oxygen starvation and the fact that it can accompany many diseases, it becomes clear that children are also affected in the affected area. Anemia, burns from fire and chemicals, gas poisoning, heart failure, various injuries, swelling of the larynx due to an allergic reaction, etc. can lead to a state of oxygen starvation of the brain in children. But most often this diagnosis is given to children at birth.
Diagnosis of oxygen starvation of the brain
Diagnosis of oxygen starvation of the brain is carried out on the basis of patient complaints, if possible, data from the words of relatives, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out.
The patient's condition is assessed based on the results of a general blood test. Indicators such as red blood cells, ESR, hematocrit, leukocytes, platelets, reticulocytes are analyzed. An analysis of the blood composition will also determine the acid-base balance of the body, the gas composition of venous and arterial blood, and therefore indicate a diseased organ.
The most accessible methods of instrumental diagnostics include pulse oximetry - a special device worn on a finger measures the level of oxygen saturation in the blood (the optimal content is 95-98%). Other means are an electroencephalogram, computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, an electrocardiogram, and rheovasography, which determines the volume of blood flow and its intensity in the arterial vessels.
Differential diagnosis
Treatment of oxygen starvation of the brain
Treatment of oxygen starvation of the brain consists of etiotropic therapy (treatment of the cause). Thus, exogenous hypoxia requires the use of oxygen masks and pillows. To treat respiratory hypoxia, drugs that dilate the bronchi, analgesics, and antihypoxanes that improve oxygen utilization are used. In case of hemic (reduced oxygen in the blood), a blood transfusion is performed, histoxic or tissue, antidote drugs are prescribed, circulatory (heart attacks, strokes) - cardiotropic. If such therapy is not possible, actions are aimed at eliminating the symptoms: regulating vascular tone, normalizing blood circulation, prescribing medications for dizziness, headaches, blood thinners, restoratives, nootropic drugs and those that reduce bad cholesterol.
Medicines
Metered aerosols are used as bronchodilators: Truvent, Atrovent, Berodual, Salbutamol.
Truvent is an aerosol can; when using, you need to remove the protective cap, shake it several times, lower the spray head down, take it with your lips and press the bottom, inhaling deeply and holding the breath for a few moments. One press corresponds to a portion. The effect occurs within 15-30 minutes. Every 4-6 hours the procedure is repeated, making 1-2 presses, this is how long the effect of the drug lasts. Not prescribed during pregnancy, angle-closure glaucoma, allergies. The use of the drug can reduce visual acuity and increase intraocular pressure.
Analgesics include a large list of drugs, from the well-known analgin to completely unfamiliar names, each of which has its own pharmacological action. The doctor will determine what is necessary in a particular situation. Here is a list of some of them: acamol, anopyrine, bupranal, pentalgin, cefekon, etc.
Bupranal is a solution in ampoules for intramuscular and intravenous injections, in syringe tubes for intramuscular injection. The maximum daily dose is 2.4 mg. The frequency of administration is every 6-8 hours. Possible side effects such as nausea, weakness, lethargy, dry mouth. Contraindicated in children under 16 years of age, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, increased intracranial pressure, and alcoholism.
The list of antidote drugs includes atropine, diazepam (mushroom poisoning), aminophylline, glucose (carbon monoxide), magnesium sulfate, almagel (organic acids), unithiol, cuprenil (heavy metal salts), naloxone, flumazenil (drug poisoning), etc. .
Naloxone is available in ampoules; there is a special form for newborns. The recommended dose is 0.4-0.8 mg, sometimes it is necessary to increase it to 15 mg. With increased sensitivity to the drug, an allergy occurs; in drug addicts, taking the drug causes a specific attack.
For strokes, Cerebrolysin, Actovegin, encephabol, papaverine, and no-spa are used.
Actovegin - exists in various forms: dragees, solutions for injections and infusions, gels, ointments, creams. Doses and method of administration are prescribed by the doctor depending on the severity of the disease. Burn wounds and bedsores are treated with external remedies. The use of the drug may cause hives, fever, and sweating. It has contraindications for pregnant women, during breastfeeding, and allergies.
Vitamins
A number of vitamins during tissue oxygen starvation are antidotes to toxic substances. Thus, vitamin K1 blocks the effect of warfarin - an antithrombosis agent, vitamin B6 - poisoning with anti-tuberculosis drugs, vitamin C is used for damage by carbon monoxide, anilines used in dyes, medicines, and chemicals. To maintain the body, it is also necessary to saturate it with vitamins.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
For general or local hypoxia of various natures, a method of physiotherapeutic treatment such as oxygen therapy is used. The most common indications for its use are respiratory failure, circulatory disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. There are various methods of oxygen saturation: cocktails, inhalations, baths, cutaneous, subcutaneous, intraband methods, etc. Oxygen barotherapy - breathing compressed oxygen in a pressure chamber relieves hypoxia. Depending on the diagnosis that led to hypoxia, UHF, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, massage, acupuncture, etc. are used.
Traditional treatment
One of the recipes for folk treatment is breathing exercises using the following method. Inhale air slowly and deeply, hold for a few seconds and exhale slowly. Do this several times in a row, increasing the duration of the procedure. Bring the count to 4 while inhaling, to 7 while holding your breath, and to 8 while exhaling.
Garlic tincture will help strengthen blood vessels and reduce their spasms: fill a third of the jar with chopped garlic, fill it to the brim with water. After 2 weeks of infusion, start taking 5 drops per spoon of water before meals.
A prepared mixture of buckwheat, honey and walnuts, taken in equal proportions, can raise hemoglobin: grind the cereal and nuts to flour, add honey, mix. Take a tablespoon on an empty stomach half an hour before meals. Fresh beet juice is also effective; it must be allowed to stand for some time before drinking so that the volatile substances are released.
Ginger will help cope with asthma attacks. Combine its juice with honey and pomegranate juice and drink a spoonful 3 times a day.
, , ,
Herbal treatment
It is effective to take decoctions, infusions, and herbal teas that have an antispasmodic effect during oxygen deprivation: chamomile, valerian, St. John's wort, motherwort, hawthorn. For problems with the respiratory system, take decoctions of medicinal mixtures from coltsfoot, pine buds, plantain, licorice root, and elderberry flowers. Hemoglobin levels can be raised with the help of herbs such as nettle, yarrow, dandelion, and wormwood.
Homeopathy
Homeopathic remedies are increasingly being used in combination with basic treatment. Here are some of the remedies that can be prescribed for oxygen starvation and are aimed at the causes of its occurrence.
- Accardium - granules containing metallic gold, arnica montana, anamyrtha coculus-like. Aimed at treating angina pectoris and cardiovascular disorders caused by heavy physical exertion. Twice a day, 10 granules half an hour before meals or an hour after, keep under the tongue until completely absorbed. The average course of treatment lasts 3 weeks. The drug has no contraindications or side effects. For use during pregnancy and children, consultation with a doctor is required.
- Atma® - drops, a complex drug for the treatment of bronchial asthma. Dose for children under one year of age: 1 drop per teaspoon of water or milk. For children under 12 years of age, 2 to 7 drops per tablespoon. After 12 years - 10 drops in pure form or in water. Continue treatment for up to 3 months. No side effects were observed.
- Vertigoheel - oral drops, used for dizziness, cerebral atherosclerosis, strokes. The drops are dissolved in water and, when swallowed, remain in the mouth for some time. Recommended from a child's age onwards. Up to 3 years - 3 drops, at the age of 3-6 years - 5, for the rest - 10 drops 3-4 times a day for a month. Hypersensitivity reactions are possible. Contraindicated for children under one year of age, during pregnancy and breastfeeding - with the permission of a doctor.
- Hawthorn compositum is a homeopathic cardiac remedy, liquid. Adults are prescribed 15-20 drops three times a day, children - 5-7 drops. The drug has contraindications in case of allergy to the components.
- Aesculus-compositum - drops, used for post-embolic circulatory disorders, post-infarction and post-stroke conditions. Single dose - 10 drops in water, holding in mouth. Frequency - 3 times a day. Duration of treatment is up to 6 weeks. Side effects are unknown. Contraindicated in pregnant women and those hypersensitive to the components of the drug.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of the heart or blood vessels may be necessary in the case of a circulatory form of oxygen starvation, the development of which occurs rapidly and is associated with disturbances in their functions.
Prevention
Prevention of oxygen starvation primarily consists of organizing a healthy daily life, which includes normal nutrition, moderate physical activity, adequate sleep, absence of stressful situations, quitting smoking and alcohol, and spending enough time in the fresh air. It is necessary to monitor blood pressure and undergo timely preventive courses for existing diseases.
Hypoxia, or as we are more often used to saying, oxygen starvation of the brain (insufficient supply of oxygen to the human body), is a fairly common phenomenon. Most often, residents of megacities, industrial zones, and those who spend a lot of time in rooms with poor ventilation suffer from a lack of clean air. This can cause serious problems in the body. We'll tell you how to recognize oxygen starvation and what you need to do to avoid complications.
CAUSES
Hypoxia can occur for a variety of reasons:
when climbing to great heights,
when working on a submarine,
foreign objects entering the respiratory tract,
attack of bronchial asthma, allergies,
carbon monoxide poisoning,
stroke, heart attack, heart disease.
Also, chronic oxygen deficiency of the brain develops in smokers, in the mountains, when working in stuffy, unventilated rooms, certain diseases (anemia, atherosclerosis), and severe stress.
SYMPTOMS
Oxygen starvation of the brain is manifested by the following symptoms:
drowsiness and lethargy (even after a long sleep),
constant headache
weakness and dizziness,
difficulty concentrating,
memory deteriorates, the speed of thought processes decreases,
pale skin, cold sweat, frequent yawning,
sudden changes in mood: irritability, apathy, sadness,
cardiopalmus,
flickering or darkening before the eyes, fainting,
convulsions,
erratic muscle activity.
PREVENTION OF HYPOXIA
To determine whether a person is truly suffering from oxygen deprivation, doctors conduct a series of tests: they take a blood test, do an electrocardiogram, electroencephalogram, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography of the brain. Next, the specialist decides what methods to use to saturate the body with oxygen. This is very important, since chronic hypoxia can lead to metabolic disorders, the development of bronchial asthma, premature aging of the body, and increases the risk of stroke.
It is in your power to prevent oxygen starvation. To do this, follow the recommendations of doctors:
spend more time in the fresh air: a leisurely walk in the park or in the forest will perfectly saturate your body with oxygen. If this is not possible, walk a couple of stops to your home, store, or work.
Regularly ventilate the room you are in: take breaks from work.
devote time to physical activity: you can start with simple morning exercises, which will awaken the body and set it up for work, improve blood circulation. It is best, of course, to exercise outdoors.
maintain a sleep schedule: an adult needs at least 7 hours of full sleep, and it is advisable to go to bed no later than 11 pm;
watch your diet: your diet must include vegetables and fruits, iron-containing foods (buckwheat, meat, brown bread, herbs, dried fruits, nuts).
Have a full rest: organize your free time so that you can spend it with pleasure, relax and gain strength.
Hypoxia is a disturbance in the oxygen supply of brain tissue, which leads to various side effects. Oxygen starvation of the brain, the symptoms and treatment of which depend on the provoking factors, is always accompanied by disturbances in the composition of the blood, as a result of which it does not flow to the brain.
Lack of oxygen can be acute or chronic, develops quickly and often causes coma. In the absence of medical care, it leads to death. All this is typical for the acute stage of the disease. In its chronic form, the pathology lasts for several months or even years.
The disease is masked behind such common symptoms as constant fatigue and low productivity. It is difficult to predict the disease, since it can develop at any age: from prenatal development to 70-90 years.
Oxygen starvation of the brain develops as a result of several factors: acute traumatic brain injury, heart block or severe failure, asphyxia, any surgical intervention on the heart, carbon monoxide poisoning, the formation of blood clots in the vessels of the brain, stroke or anemia, respiratory diseases.

These reasons accompany acute hypoxic brain damage. In the chronic form, factors such as living in unfavorable environmental conditions and high mountainous areas are more often found. Also, a chronic process develops as a result of atherosclerotic formations that impair blood flow.
When the blood vessels are completely blocked, the death of brain tissue and cerebral infarction begin. The most serious danger posed by cerebral hypoxia is death. Because the disease develops very quickly, the mortality rate once diagnosed is quite high.

General manifestations of the disease
When drawing up a clinical picture, the symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain are accurately determined by the attending physician. This condition is characterized by:
During diagnosis, slight changes in brain structures are observed, which cause a state of euphoria and uncontrolled behavior. The patient is restlessly agitated and cannot control himself.

Stage of external changes. The patient's skin turns pale, bluish swelling or severe redness appears. At this stage, the brain tries to restore blood circulation, resulting in perspiration on the forehead and cold sweat throughout the body.
Oxygen starvation of the brain is accompanied by severe disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system. At this stage, the brain structures are significantly damaged, resulting in: severe vomiting, dizziness, and nausea. Vision deteriorates, its clarity is impaired, in some cases, attacks of darkening occur in the eyes, and patients lose consciousness.

Perinatal damage at a severe stage. Brain swelling develops, which leads to a vegetative state: the patient loses all reflexes and may fall into a coma. The sensitivity of the skin and the functioning of all internal organs are impaired.
At all stages except the initial stage, the patient is accompanied by severe weakness and drowsiness.
Chronic oxygen deprivation of the brain leads to frequent headaches and tinnitus. The patient experiences fatigue, morning sickness, problems with concentration and attention, and memory impairment. During diagnosis, disturbances in the functioning of various organs are detected.
Hypoxic hypoxia of the brain develops with low oxygen supply for a long time without the influence of pathological processes.
This form of pathology appears in people who spend a lot of time in enclosed spaces without access to natural air (bunkers, tanks, submarines). It can be observed in those who spend a long time in high mountains. The condition is often recorded in people who frequently and quickly ascend on airplanes and spacecraft.
With a lack of oxygen, the concentration of hemoglobin decreases, the excitability of the respiratory centers increases, which leads to hyperventilation of the lungs. With this form, the water-salt balance often changes and vascular tone worsens.

Symptoms of hypoxic disease in adults are:
- rapid breathing and shortness of breath even at rest, as well as during physical exertion;
- an inexplicable surge of energy, acceleration of movements, speech;
- low performance;
- problems with short-term memory;
- paresis, drowsiness, inhibition of reactions as the disease progresses.
In the final stages, possible loss of consciousness, convulsions, involuntary urination and coma. If the activity is associated with an elevation of 9-11 km above sea level, then acute symptoms from the cardiac system appear. The result may be breathing problems that lead to coma and death.
Comatose hypoxia of the brain begins 40-50 seconds after the cessation of oxygen supply. Brain death may occur within 5 minutes. The first signs of coma include:
- inhibition of the cortex– the patient loses orientation in time and space, reactions to any stimuli worsen. Uncontrolled emptying of the bladder and bowels occurs. A person’s heart begins to beat rapidly, and accompanying reflexes are inhibited. However, breathing is still maintained and artificial ventilation is not required;

- anterior brain dysfunction manifested by convulsions, lack of speech, high or sharply low blood pressure, as well as weak pupillary response;
- , in which the medulla oblongata is affected. In this case, there is a complete absence of reaction to external factors, muscle tone decreases, the functioning of the respiratory system deteriorates, pressure decreases and convulsions occur;

- terminal coma– the brain stops working completely. The temperature and pressure drop sharply, the person needs artificial ventilation, reflexes disappear and atony appears.
Coma at stage 4 is accompanied by a high risk of death - up to 90% of all cases.
Consequences of fasting
Even with timely assistance, brain hypoxia can lead to various consequences:
- persistently deteriorated blood circulation, including in the lungs;
- temporary oxygen starvation leads to loss of hearing, vision, heart pain and weak immunity;
- prolonged cerebral hypoxia leads to serious heart diseases, including heart attack, failure, angina pectoris, stroke;
- with a long-term form of the disease, metabolism in cells deteriorates, which leads to diabetes, obesity and endocrine disorders;
- the risk of oncological processes and benign tumors increases.

Prolonged brain hypoxia prevents normal recovery of the body. Some of the dead tissue is no longer regenerated.
Does the brain recover after illness?
Even partial hypoxic changes in the brain lead to the death of certain tissues and cells. However, timely therapy reduces these damages by up to 90%, preserving normal human viability.
Brain cells have an unusual ability - they easily take over the functions of neighboring particles. But restoration of dead tissue is impossible; “infection” with usual functions develops only in partially damaged structures.
A long-term lack of help necessarily leads to irreversible consequences. This is why it is so important to diagnose and begin treatment for brain hypoxia.
Medicinal methods of eliminating the disease
To treat oxygen deprivation, different groups of medications are used, including drugs to ease breathing, painkillers, and medications to stimulate blood circulation:
- "Truvent". Used to dilate the bronchi. “Berodual”, “Salbutamol”, “Atrovent” have a similar effect.

- Analgesics. For treatment, any available means indicated by the doctor are used. Often prescribed: "Bupranal", "Pentalgin", "Anopyrin", "Akamol".
- Antidote drugs. Used to treat hypoxia caused by poisoning: Unithiol, Cuprenil for heavy metal intoxication, Flumazenil for drug poisoning.
Almagel and magnesium sulfate are used to combat organic acid poisoning, and glucose is used to treat carbon monoxide poisoning. "Atropine" and "Diazepam" are prescribed for the treatment of mushroom poisoning.
- State of —stroke—. Antispasmodics are used for treatment.

Vitamins are prescribed to treat various conditions. If oxygen starvation of the brain is a consequence of poisoning, then vitamins B6, K1, C are prescribed. Multivitamin complexes are used in the treatment of the disease in almost all cases.
Physiotherapy
Any hypoxia of the brain responds well to physiotherapeutic procedures, the main of which is oxygen therapy. It is indicated for respiratory failure, vascular and circulatory problems. Your doctor will tell you how to saturate the brain with oxygen and choose the appropriate method.
There are several of them: baths, subcutaneous and subcutaneous injections, cocktails, inhalations. Oxygen barotherapy is an effective method of breathing compressed oxygen in a special pressure chamber.

Laser therapy, UHF method, magnetic therapy and massage are also used. Brain hypoxia is treated with oriental medicine, which uses methods such as acupuncture, exercise, herbal teas and natural medicines.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine specialists suggest doing gymnastics during oxygen starvation (for example, the Strelnikova method), and taking garlic tincture to treat spasms. Traditional methods can restore low hemoglobin: buckwheat is mixed with honey, walnuts, and ginger. A mixture with olive oil, ginger and honey will help against atherosclerosis.

Oxygen starvation of the brain is eliminated by treatment with herbs (infusions, decoctions). St. John's wort, valerian, chamomile, hawthorn and motherwort have antispasmodic effects.
If the respiratory system is affected, then you can take pine buds, coltsfoot, plantain, elderberry and licorice root. And dandelions, wormwood and yarrow will be useful for hemoglobin.
Homeopaths suggest treating oxygen deprivation of the brain with accompanying methods:
- "Accardium". Medicinal granules made from mountain arnica, anamyrtha and metallic gold. Used for pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
- "Atma". Stimulating drops for asthma and breathing problems.
- "Hawthorn-compositum". A remedy for cardiac problems.
- "Vertigoheel". Drops for atherosclerosis and dizziness, used for the prevention and treatment of strokes.
- "Esculus-compositum". Drops are used for circulatory problems, after strokes.

Cerebral hypoxia is treated mainly surgically.
Any form of oxygen starvation requires emergency treatment. Symptoms of the disease develop quickly and can cause death and permanent brain damage. It is mandatory to go to the hospital if there are signs of hypoxia.
Also, the cause may be various disruptions in its functioning - there are situations when cells fail to absorb oxygen. In any case, the body's cells do not receive enough oxygen.
Symptoms
Causes
- in case of carbon monoxide poisoning;
- with large blood loss;
Treatment
Consequences
Lack of oxygen entering the brain causes pathological disorders and coma. The most serious consequence is death. Severe cerebral hypoxia leads to death in just a few minutes.
Why is brain hypoxia dangerous?
How to determine hypoxia
What causes a subependymal brain cyst in newborns, consequences and removal
Is a cerebral pseudocyst dangerous in a newborn and how to get rid of it?
Symptoms and treatment of cysts of the transparent septum of the brain
Causes of cerebral gliosis, likely consequences, treatment
What are cystic-gliotic changes in the brain, why is it dangerous?
What causes brain atrophy, how to deal with tissue transformation
What is oxygen starvation of the brain (hypoxia)?
Oxygen is something without which our body cannot live for even a few minutes. All human organs without exception are sensitive to its deficiency. But the most sensitive is the brain. Oxygen starvation, or hypoxia, leads to damage to its cells within a few seconds; after 20 seconds, a person falls into a coma, and after 4 minutes, brain death occurs. Therefore, it is so important to understand why oxygen starvation of the brain occurs and what hypoxia can lead to.
Types of oxygen starvation
Depending on how quickly oxygen starvation develops, hypoxia occurs:
- Spicy. The occurrence of obstacles to the blood supply to brain tissue. May appear as a result of large blood loss, poisoning or heart attack.
- Chronic. May occur in patients with cardiosclerosis, heart failure and other heart diseases.
- Lightning fast. It is developing rapidly. The duration of this hypoxia phase can last several seconds or minutes.
Depending on what caused the disorder, the following forms of hypoxia are distinguished:
- Exogenous. Occurs when a person inhales air with low amounts of oxygen.
- Respiratory. The cause is various disturbances in the functioning of the body, which prevent the supply of the amount of oxygen necessary for the brain.
- Circulatory. This form can be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the heart or blood vessels. Characterized by rapid development.
- Fabric. Appears due to a violation of the absorption of oxygen by the tissues of our body.
- Hemic. It is a consequence of a decrease in the amount of oxygen dissolved in the blood.
- Reloading. It occurs in people when the amount of oxygen that enters the body does not fully satisfy its need. May occur during heavy physical exertion.
- Mixed. Most often it develops gradually and can have serious consequences. It arises as a result of a whole complex of negative factors.
Reasons that provoke oxygen starvation of the brain
The most common causes of hypoxia in adults are:
- A stroke, which results in acute oxygen deficiency in one of the hemispheres of the brain.
- Stressful situations accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure.
- Anemia.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Staying for a long time in a closed, unventilated room or when rising to a high altitude (to the mountains).
- Gassing.
- Cardiac arrest, which leads to the cessation of oxygen supply to the brain tissue.
- Heart failure.
- Paralysis or respiratory diseases.
- Suffocation.
- Various circulatory disorders of the body.
- Reaction to alcohol.
- Complications after surgery.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- An allergic reaction that contributed to the development of laryngeal edema.
Symptoms of the disease
Oxygen starvation of the brain in adults has standard symptoms that often help with diagnosis. These include:
- Increased excitability, which has not been observed before. A slight oxygen deprivation of the brain provokes a state of euphoria; a person may not control his behavior. Excitability gives way to lethargy and a feeling of depression.
- Sharp headache. Most often it has a pressing character.
- Arrhythmia and tachycardia.
Find out more about the causes and symptoms of the disease from Vladimir Matveevich Podkhomutnikov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Department of Cardiology of the Novokuznetsk State Institute:
- Change in skin color. It becomes pale and may have an overly red or bluish tint. In such a situation, the brain tries to restore normal blood supply, which can manifest itself as increased sweating.
- Slowness of the nervous system, which is a manifestation of post-hypoxic brain damage. In this case, the patient notes dizziness, nausea or uncontrollable vomiting. At the same time, vision may be impaired and darkening of the eyes may occur. Hypoxia provokes loss of consciousness.
- Perinatal brain damage as a consequence of oxygen starvation. This condition provokes cerebral edema, and the patient’s conditioned and unconditioned reflexes disappear. If the blood supply to the brain is not restored, the functioning of all internal organs is disrupted, and the skin stops responding to external stimuli.
Diagnosis of hypoxia
To make a diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out:
- Pulse oximetry. This diagnostic method is rightly called the most accessible way to determine cerebral hypoxia. To do this, a special device, a pulse oximeter, is placed on the patient’s finger.
- Study of acid-base balance. The method is based on an analysis of blood composition, which allows one to evaluate the quantitative indicators of many body functions.
- General blood test (if you are a resident of St. Petersburg, then here http://medi-center.ru/laboratornaya-diagnostika/analizy-v-spb you can make an appointment).
- Electroencephalogram.
- Computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
- Electrocardiogram.
- Rheovasography.
Depending on the patient’s health status, the degree of hypoxia and the suspected cause of oxygen deficiency in the brain, the doctor will prescribe an individual diagnostic program.
Treatment of oxygen starvation of the brain
Before starting treatment for oxygen starvation in adults, it is necessary to establish the exact cause that provoked this condition. Therefore, it is important for the patient to clearly formulate the factors that could lead to this. Most often in an adult it is smoking, alcohol abuse, and prolonged stay in a poorly ventilated area.
Having assessed the severity of oxygen starvation, the doctor will recommend treatment in a hospital or at home. The patient is prescribed medications that stabilize the normal functioning of the body. It is also necessary to take medications whose action is aimed at restoring normal blood supply to brain tissue.
Sometimes, to relieve symptoms of mild oxygen starvation, it is enough for an adult to ventilate the room in which he is located or go outside. The situation is different if the cause is some kind of disease or disruption of the body.
If oxygen starvation provokes a disease of the blood, cardiovascular or respiratory system, the patient will require more serious measures to eliminate it.
- For exogenous hypoxia, oxygen equipment (masks, pillows, etc.) is used.
- To treat respiratory hypoxia, analgesics, antihypoxanes and drugs that dilate the bronchi are used. Sometimes artificial ventilation is performed.
- Hemic hypoxia requires blood transfusion, which helps normalize blood circulation.
- With a circular form of oxygen starvation, surgical intervention on the heart or blood vessels is necessary.
- To treat the histoxic form, antidote drugs are used.
If the patient sees a doctor in time and is prescribed effective treatment, the prognosis for recovery will be favorable. However, if oxygen deprivation continues for a long period of time, irreversible consequences may develop that cannot be eliminated.
You can learn interesting facts about the disease from pediatrician, family doctor Konstantin Borisovich Zabolotny:
Folk remedies for the disease
Along with traditional methods of treatment, folk remedies are often prescribed that help restore blood supply to brain tissue. Decoctions of rowan fruits, horsetail herbs, motherwort, wood lice and periwinkle have proven themselves to be effective.
As an example, we can give a recipe for a folk remedy made from crushed woodlice leaves. To prepare such a tincture, take 1 tablespoon of the herb, pour 1 glass of boiling water, stir, cover the container with a lid and leave to infuse for 7-8 hours. Take this medicine 50 ml 30 minutes before meals.
But it is worth noting that before taking any folk remedy, you should consult a doctor, as some of them can cause allergic reactions.
Consequences of hypoxia
When making a prognosis for a patient, doctors focus on the degree of damage to brain tissue, which depends on how long the brain has been starved of oxygen.
If the lack of oxygen does not last long, the prognosis is usually favorable and the patient manages to eliminate its consequences. But if hypoxia is left untreated for a long time, it can lead to the development of a vegetative state. In this state, the patient retains the basic functions of the body (breathing, blood pressure, etc.), but the person will not respond to what surrounds him. As a rule, such patients live within 1 year.
Oxygen starvation in some patients leads to loss of appetite, blood clots and the development of pulmonary infections.
Hypoxia in newborns
Oxygen deficiency in brain tissue can occur in a newborn at any stage of its development: during childbirth or even during intrauterine development. Hypoxia is one of the most commonly diagnosed disorders in newborns.
The following factors can influence the occurrence of oxygen starvation:
- Maternal illness, severe pregnancy and childbirth. The fetus may lack oxygen due to anemia or heart defects of the pregnant woman, premature abruption of the placenta, or bleeding from the placenta.
- Pathologies of blood flow through the umbilical cord and impaired placental-uterine circulation. This also includes entanglement with the umbilical cord, damage to its vessels, trophic disorders of the placenta, prolonged or rapid labor, and the use of special medical instruments (forceps, etc.).
Gynecologist Raisa Zanitullina talks about fetal hypoxia in this video:
- Genetic abnormalities in the fetus, anomalies of its development, Rh conflict, infectious diseases, congenital heart disease, skull injuries.
- Asphyxia, as a result of which the fetal airway is partially or completely blocked.
After birth, the baby must be examined by a neonatologist, who can pay attention to the symptoms of oxygen starvation in the newborn. In this case, the baby experiences tachycardia. Subsequently, it turns into arrhythmia and heart murmurs. A child who has suffered hypoxia may develop blood clots and numerous hemorrhages in tissues and organs.
Treatment of the disease in newborns
Treatment of children differs significantly from treatment of adult patients. If there is a suspicion of a lack of oxygen in the fetus, doctors try to speed up labor without harming the mother and baby. This can be done by caesarean section or by using obstetric forceps. After the child is removed, everything possible is done to provide him with the necessary amount of oxygen.
During childbirth, doctors can use special medications, the effect of which is aimed at increasing blood circulation in the placenta and the human body. A set of resuscitation measures is also often used to clear the newborn’s airways of mucus and perform artificial respiration.
Until the child’s condition stabilizes, he is advised to administer the following drugs: sodium gluconate, glucose solution, etimizol. In the future, a child who has suffered hypoxia should be under the supervision of a pediatrician and a neurologist, who will monitor his development and, if necessary, correct possible changes in the body’s functioning.
However, doctors are not always able to provide effective therapy that would help the baby completely get rid of the consequences of oxygen starvation. In this case, the child remains disabled. This leads to a delay in physical or mental development. Therefore, doctors always recommend that pregnant women carry out prevention, which consists of a balanced diet, taking vitamins, frequent exposure to fresh air, and light exercise that will correspond to the specific stage of pregnancy.
Hypoxia is not a disease, but a condition that can be effectively treated. Only for this, it is necessary to identify the pathology in time and begin the correct treatment.
Lack of oxygen in the brain symptoms
in DiseasesViews
Doctors call oxygen starvation of the brain hypoxia. This condition occurs as a result of insufficient oxygen supply to the human body. Also, the cause may be various disruptions in its functioning - there are situations when cells fail to absorb oxygen. In any case, the body's cells do not receive enough oxygen.
The first symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain must be responded to immediately. Signs of starvation of the human brain from oxygen deficiency in the first stages may be almost imperceptible, but subsequently can cause irreparable damage to the entire body.
- A person experiences a sharp excitement in the body, an increase in adrenaline and a state of euphoria. Then, this state quickly turns into lethargy, lethargy and fatigue. After a surge of strength, people feel very tired and apathetic. In this state, you feel very dizzy, your heart rate increases, cold sweat appears, and convulsions may occur.
- Sudden deterioration of memory, a person may not be able to navigate his location and suddenly forget where he was going and what he wanted to do. People experience confusion and even disorientation. This condition quickly passes, having calmed down, people do not pay much attention to it, attributing their condition to fatigue, overwork or prolonged fasting.
- A symptom of hypoxia can be caused by a sharp headache. This occurs due to pressure differences and a long stay in a stuffy room.
- Loss of sensitivity in various parts of the body. An arm or leg may not obey, or involuntarily perform uncontrollable actions. After recovery, people experience feelings of lethargy and pain in their limbs.
- Nervousness increases sharply. A person wants to cry or laugh for no apparent reason.
- Symptoms of brain oxygen deficiency include sleep disturbance. People suffer from insomnia. They often wake up in the middle of the night and cannot sleep for a long time.
- General fatigue of the body. The person feels overwhelmed and cannot concentrate on certain work. Irritability and aggression appear.
- Violation of visual and speech functions of the body. People cannot pronounce a few words coherently.
Oxygen starvation of the brain can be caused by a long stay at great depths, being at a height, being in a very polluted room, a severe lack of oxygen or asphyxia, or being in a stuffy room for a long time.
All symptoms indicate a sharp deterioration in brain performance and can lead to serious disruptions in the functioning of the entire human body. It is necessary to pay attention to the symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain and immediately contact a specialist. Early diagnosis and timely treatment will prevent deeper diseases.
Find out what the consequences of cerebral hemorrhage are and how to avoid them
Subarachnoid hemorrhage in newborns here
In this article you will learn what are the causes of cerebral encephalitis http://golovnojmozg.com/bolzn/entsfl/ents-golovnogo-mozga.html
The reasons for oxygen starvation of the body are different. This condition may occur:
- when the volume of oxygen in the air that a person inhales decreases (this phenomenon is observed when climbing mountains or when staying in poorly ventilated rooms);
- when there is a mechanical obstruction to the flow of air into a person’s lungs (observed when the airways are closed with water or vomit, or when the nasal passages are narrowed as a result of an allergic reaction);
- in case of carbon monoxide poisoning;
- with large blood loss;
- when taking certain medications;
- with a lack of vitamin B2 as a result of liver cirrhosis or hepatitis.
In addition, a condition in which oxygen starvation of the brain and heart occurs is caused by coronary artery disease, thrombosis, vascular spasms and smoking.
In any case, a person suffering from oxygen starvation of the brain needs emergency help. When the first symptoms appear, you must immediately call a doctor, and before his arrival, provide the patient with an influx of fresh air. You need to unfasten tight clothes, perform artificial respiration, pour water out of your lungs, and take them out of the smoky room into fresh air.
Doctors then ensure that the body is oxygenated. In particularly severe situations, a blood transfusion may be necessary. If necessary, a person is prescribed decongestants, as well as various therapeutic procedures. To treat hypoxia in newborns, they are placed in a special chamber, resuscitation measures are carried out, and nutrient solutions are administered.
Consequences
The brain cannot tell the heart to beat faster or slower. The functioning of the heart is controlled by the cells of the body's tissues. Oxygen serves as a tool for controlling heart pulsation. When there is a lack of oxygen, cells require blood saturated with it. The heart speeds up its work and muscle tension. This increases the speed of blood flow and blood pressure.
As soon as the required amount of oxygen arrives, the cells relieve their demands, and the heart switches to a calm mode of operation, the pain subsides. Only daily gymnastics, feasible physical work and proper nutrition can ensure good capillary permeability. A person should spend 1/10 of his daily time to ensure good health.
When you inhale, air enters the lungs and expands the alveoli. If the inhalation is weak, then a small part of the alveoli moves apart, and not the entire surface of the blood vessels comes into contact with the incoming air. In this case, the lungs will not provide the body's need for oxygen.
With a large, energetic inhalation, the alveoli will be pressed against each other, the blood vessels will be compressed, their area in contact with the air will decrease, and the movement of blood in them will slow down. Blood oxygen saturation will be low - acute oxygen starvation will occur. The person may become dizzy and lose consciousness. You need a comfortable, free breath that fills the lungs completely.
Weak inhalation and excessive filling of the lungs with air cause unsatisfactory oxygen saturation of the blood.
Everyday breathing is breathing in which a constant sequence of inhalation, exhalation and pause is observed. This is common, a person breathes this way from birth to death, but the body’s need for oxygen is not always met.
Oxygen starvation of the body occurs when the oxygen content in the inhaled air decreases, the body is in a painful state, metabolism in cells is activated, heavy physical work is performed, nervous overexertion, food consumption is excessive and the body is aging. A person does not immediately feel oxygen starvation. He does not pay attention to discomfort in the body, malaise, changes in blood pressure and pulse, profuse sweating, unexpected pain in the heart and head, etc.
With temporary oxygen starvation, blood pressure changes, arrhythmia, headaches and heart pain occur, vision and hearing deteriorate, and the body’s self-defense functions decrease.
With prolonged oxygen starvation, in addition to the symptoms of temporary oxygen starvation, diseases arise:
- heart, circulatory system (angina pectoris, heart failure, heart attack, varicose veins), brain (stroke), etc.;
- metabolism in cells - obesity, diabetes, liver disease, etc.;
- body defense systems (tumors of various etiologies).
Prolonged oxygen deprivation suppresses the body's ability to heal itself.
Oxygen starvation of the brain (hypoxia) in adults
Oxygen starvation of the brain (or hypoxia) is a pathological condition that develops due to insufficient oxygen supply to the nervous tissues. This happens for two reasons: due to a lack of oxygen in the blood or due to impaired blood supply to the brain.
Hypoxia can be acute or chronic. In the first case, there is a sharp cessation of oxygenation of the brain, which can result in irreversible changes in the nervous tissue and even death. Chronic hypoxia develops over months and years, manifesting itself as symptoms of chronic fatigue and decreased ability to work.
Causes of oxygen starvation
In an adult, the following pathological conditions can cause acute cerebral hypoxia:
- Stroke. With this disease, one part of the brain usually suffers, located in the area of the blood supply to the affected vessel (during a stroke, it becomes clogged with a blood clot, narrows or ruptures).
- Shock. Any shock is accompanied by a sharp decrease in blood pressure, and accordingly the brain is less well supplied with blood and oxygen.
- Cardiac arrest and, as a consequence, cessation of blood circulation through the vessels.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning. in which hemoglobin stops carrying oxygen to tissues.
- Asphyxia or suffocation. With this pathology, the blood in the lungs is not enriched with oxygen, and accordingly the brain begins to suffer from hypoxia. Asphyxia occurs when hard and soft objects, water, enter the respiratory tract, during a spasm of the respiratory tract (for example, during an allergy, an attack of bronchial asthma), during a mechanical impact on the neck - hanging and strangulation by hand.
Chronic oxygen deficiency of the brain develops:
- For certain diseases (anemia, diseases of the respiratory system accompanied by respiratory failure, atherosclerotic damage to cerebral vessels).
- When working in unventilated, smoky areas.
- In the mountains (where there is low oxygen pressure in the air).
What happens in the brain during hypoxia?
The depth of pathological changes in brain tissue depends on the severity of hypoxia. Thus, in acute severe oxygen deficiency against the background of swelling of the brain, irreversible transformations in neurons develop quite quickly. And even after the supply of oxygen to the brain is resumed, these processes continue, leading to complete destruction of cells and the formation of softened lesions in the brain tissue. All this is subsequently manifested by various neurological disorders.
If, during acute hypoxia, the patient receives timely assistance, the likelihood of severe complications is minimized - the cells simply do not have time to suffer much and gradually return to their normal state.
Well, chronic hypoxia is generally not characterized by pronounced morphological changes in nerve cells, so the health of such patients is restored quickly, provided that the influence of etiological factors on the body ceases.
Symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain
The clinical picture of acute and chronic oxygen deficiency in the brain is radically different.
With symptoms of hypoxia in acute form, emotional and motor arousal are first noted. This stage is also characterized by rapid heartbeat, cold sweat, pallor, and “flying spots” before the eyes. Gradually, drowsiness, general lethargy, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, stupor and loss of consciousness appear, and there may be convulsions. The extreme degree of brain hypoxia is coma. In severe oxygen deficiency, it develops within minutes after loss of consciousness.
Chronic brain hypoxia has its own number of characteristic symptoms: constant fatigue, headache, sleep disturbance, dizziness, depressive disorders. Pathological changes in hearing and vision may appear. All this negatively affects a person’s ability to work.
Treatment of acute hypoxia
Treatment for oxygen deprivation of the brain involves maintaining the activity of the cardiovascular and respiratory (or respiratory) systems. In addition, the acid-base state of the body is normalized, since acidosis (increased acidity) that develops during hypoxia leads to even greater hypoxic tissue damage.
Also, methods such as general and craniocerebral hypothermia (a deliberate decrease in body and brain temperature, which slows down tissue metabolism), and hyperbaric oxygenation are widely used to treat brain hypoxia. With increasing swelling of the brain, decongestants are indicated.
To improve cerebral circulation, the patient is prescribed drugs that correct microcirculation, antioxidants, and vasodilators. To restore nerve cells - neuroprotective agents, nootropics, antihypoxants.
Further treatment tactics for patients with acute cerebral hypoxia are determined by the causes of this pathology and the severity of neurological disorders.
Treatment of hypoxia in chronic form
In case of chronic lack of oxygen, it is necessary to eliminate the factors that cause it. If possible, change working conditions.
- For diseases of the respiratory tract, follow all doctor’s recommendations, undergo courses of treatment so that the lungs and bronchi function fully and the body receives a sufficient amount of oxygen.
- If there is a suspicion that the ailments are due to anemia, you should be examined and treated. Of the drugs that increase hemoglobin, the most effective are Ferrum Lek, Totema, Aktiferrin, Ferlatum, Solgar.
- For atherosclerosis, long-term use of special drugs that improve blood circulation in the brain, such as Cinnarizine, Actovegin, Vinpocetine (also Cavinton, Cavintex), Tanakan, is indicated.
- Natural medicines for hypoxia include those containing Ginkgo biloba extract, which improves cerebral circulation, increases mental performance, develops memory and attention, and can also reduce meteosensitivity.
- When treating oxygen starvation of the brain, taking the amino acid Glycine is indicated. It affects mental and physical performance, helps to remember better, reduces psycho-emotional stress, and has an antidepressant and anti-stress effect.
Video: hypoxia and its consequences
Diagnosis of cerebral hypoxia - the dangers of oxygen deprivation
Brain hypoxia - what is it?
In simple terms, hypoxia is oxygen starvation. The human brain has a large number of blood vessels that supply various sections with nutrients. Brain tissue is sensitive to loss of oxygen.
There are three types of hypoxia: fulminant, acute, subacute and chronic.
- Lightning oxygen starvation - develops quickly, lasting only a few minutes or seconds.
- Acute deficiency - develops due to severe poisoning, blood loss, and heart attacks. With this diagnosis, the blood loses its ability to transport oxygen.
- Chronic hypoxia – the cause of hypoxia is heart failure, heart defects, cardiosclerotic changes.
The negative effect of hypoxia on the brain is tissue death and loss of functionality. The consequences of oxygen starvation depend on the duration of the disorders, as well as the complications caused by them.
Causes of oxygen starvation of the brain
Symptoms of brain hypoxia depend on the causes of oxygen starvation. The etiology of disorders includes several main factors that provoke pathological changes:
- Exogenous - occurs due to low oxygen content in the air. Occurs when rising to a height, staying in a closed room for a long time, or low air pressure.
- Tissue – characterized by impaired metabolism of the body. As a result of the disorders, the soft tissues are not able to adequately absorb the oxygen supplied by the blood.
- Respiratory – appears due to respiratory disorders and the inability to obtain sufficient oxygen naturally.
- Circulatory – develops as a result of disorders of the cardiovascular system. The fight against brain hypoxia is aimed at improving blood circulation. By normalizing the functioning of the heart, blood vessels and arteries, and restoring normal metabolism, it is possible to significantly improve the patient’s condition.
- Hemic - manifests itself in patients with a reduced ability of the blood to transport oxygen. Observed due to the development of anemia.
Hypoxic changes in the brain in newborns occur due to trauma during pregnancy, developmental abnormalities and insufficient supply of nutrients to the developing fetus.
How does a lack of oxygen manifest itself in the brain?
Symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain make it possible to accurately determine the presence of disorders. The attending physician will pay attention to the following deviations:
- Stage of increased excitability - moderate post-hypoxic changes in brain structures lead to a state of euphoria, the ability to fully control one’s actions and movements is lost.
- Change in skin color - a person’s skin becomes pale, with a bluish tint, or becomes excessively red. The natural reaction of the brain to hypoxia is to restore normal blood supply and metabolism.
A symptom of the brain’s attempts to correct disturbances is the appearance of cold sweat and perspiration.
At the same time, there is a violation of visual functions: clarity of vision, darkening of the eyes. The development of oxygen starvation leads to loss of consciousness.
With increased sensitivity of the brain to hypoxia, the condition is accompanied by coma.
Under normal conditions, the human brain consumes 25% of the total amount of oxygen and glucose absorbed by the body. Any deviations lead to hypoxia and serious, often irreversible consequences.
Why is brain hypoxia dangerous?
Oxygen starvation is a dangerous condition that leads to pathological changes that affect brain activity, as well as disruption of its basic functions. The prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of damage and the time during which hypoxia was observed.
With a short-term coma, the chances of rehabilitation are quite high. It takes a long time for brain cells to recover from hypoxia, but ultimately a patient who does not fall into a coma has a good chance of recovery.
A prolonged vegetative state with preservation of the basic functions of the body leads to serious disorders. Patients in a coma usually live no more than a year before dying.
In addition, oxygen starvation manifests itself in the following clinical symptoms:
Consequences in adults are associated with the difficulty of restoring even minimal motor and speech functions. Prolonged oxygen starvation leads to coma and death.
Post-hypoxic brain changes
The consequences of brain hypoxia after clinical death include loss of neurological functions. After the patient returns to life, the doctor’s task is to determine the presence of irreversible changes.
After clinical death, coma or prolonged oxygen deprivation, the predicted results of therapy may differ.
- Complete restoration of brain function – rapid or delayed recovery of functions is observed. Normalization of the condition occurs within several days or months. Possible deterioration in health.
Interrupted recovery is also diagnosed, in which a rapid improvement in well-being occurs. In this case, after several weeks or months, secondary deterioration occurs, transforming into persistent neurological dysfunction.
Treatment of cerebral hypoxia is fraught with difficulties. Full recovery is extremely rare, but with proper therapy, stable remission can be achieved.
Does the brain recover after hypoxia?
Brain cells do not recover after hypoxia. But with properly prescribed therapy, it is possible to provide the proper conditions for normalizing the daily functions of the body.
Brain tissues have the ability to take over the functions of neighboring cells. However, any restoration is carried out partially.
An adult needs to combat brain hypoxia from the first manifestations of the disease. All disturbances in cell functioning are critical and lead to serious and often irreversible consequences.
Brain hypoxia in newborns
The share of congenital pathologies and hypoxia accounts for about 30-35%. This pathology occurs due to oxygen starvation of the fetus during development in the womb. Lack of oxygen in the brain in a newborn leads to abnormalities in the development of internal organs: lungs, liver, cardiovascular and central nervous systems.
What causes a baby's brain to lack oxygen?
As already noted, it is the blood that supplies oxygen to the brain. Responsible for transporting the nutrient element - hemoglobin. To create a sufficient amount of this substance, a large amount of iron elements is required.
With anemia, iron deficiency is observed, and accordingly, the rate and intensity of oxygen supply to the body tissues decreases. Mild insignificant hypoxia in newborns usually occurs if the mother suffers from anemia.
The second main reason is related to placental insufficiency. Through the placenta, the mother nourishes the embryo and supplies it with oxygen. A metabolic disorder blocks normal metabolism.
Insufficient oxygen saturation of the brain vessels of the developing fetus, due to placental insufficiency, occurs for the following reasons:
- Bad habits.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Stress.
- In premature babies.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Intrauterine infections.
- Prolonged compression of the fetal head.
- Birth injuries.
The diagnosis of fetal hypoxia is made in approximately 10-15% of pregnancies. The doctor delivering the baby will pay attention to the condition of the newborn. The prerequisites for cardiac monitoring and additional examination are:
- Turbid waters with a greenish tint.
- Entwining the fetus with the umbilical cord.
- Premature placental abruption.
Signs of post-hypoxic changes in the brain in a newborn manifest themselves in characteristic symptoms: neurological seizures, disruption of life rhythms, irritability and tearfulness. In combination with the results of ultrasound of the newborn’s brain and medical history, an accurate diagnosis of the presence of oxygen starvation can be made.
What consequences can hypoxia cause in an infant?
The consequences of neonatal hypoxia depend on the degree of damage and the presence of irreversible changes in the central nervous system. With mild damage, complications manifest themselves in the development of perinatal encephalopathy.
Cerebral edema in a newborn due to hypoxia leads to disability and, unfortunately, death. With a favorable outcome, it is possible to partially restore basic functions. Developmental problems are possible: restlessness, hyperactivity, low concentration, speech disorders.
What and how can you treat hypoxia?
The main task of medical personnel is to restore normal oxygen supply to the brain, as well as stabilize the patient’s condition. To provide proper treatment, it is necessary to recognize disorders, provide first aid and prescribe adequate therapy.
How to determine hypoxia
Medical personnel have various research methods at their disposal that make it possible to diagnose disorders even at an early stage.
The following types of laboratory and instrumental methods are traditionally used:
- Ultrasound - echography of hypoxic changes - is a fairly reliable method, widely used to diagnose deviations from the norm during the intrauterine development of a child. The method allows you to determine oxygen starvation even at an early stage.
Echographic signs of hypoxic brain damage indicate the total volume of necrotic phenomena in adults, and make it possible to make an approximate prognosis of the development of the disease.
To get rid of oxygen starvation, it is necessary to accurately determine the catalyst for the disorders. If the cause of hypoxia is not eliminated, a relapse of the disease will certainly occur.
First aid for lack of oxygen in the brain
Oxygen starvation manifests itself in fainting and loss of consciousness. When the first symptoms of disorders appear, it is necessary to provide the patient with unhindered access to fresh air.
In medical conditions (for example, with intrauterine vascular hypoxia), an oxygen mask is immediately used after birth. If this is not possible, you should ventilate the room, free the patient from clothing that interferes with the full performance of the respiratory function. Immediately after this, the patient should be hospitalized in the nearest hospital.
Medicines for oxygen starvation of the brain
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the causes of hypoxia. In any case, iron supplements and a vitamin complex are prescribed, which improve tissue metabolism and hematopoiesis.
In severe cases of cerebral hypoxia, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Bronchodilators.
- Respiratory analeptics.
- Antihypoxanes.
Along with drug treatment, blood transfusions and artificial ventilation are used. In some cases, surgery is indicated.
Breathing exercises for hypoxia
One of the most effective means of increasing the brain’s resistance to hypoxia is the use of breathing exercises. Several types of different techniques have been developed aimed at combating pathological abnormalities.
- Strelnikova's method.
- Bodyflex gymnastics.
- Eastern gymnastics.
- The principle of oxygen starvation or the system of healthy breath holding.
The selection of a method of health-improving gymnastics should be carried out together with the attending physician, depending on the patient’s diagnosis. Breathing exercises serve as a good preventive measure to prevent complications from hypoxia.
Folk remedies for hypoxia
Folk remedies are aimed at saturating the cerebral cortex affected by hypoxia with nutrients by improving metabolism and hematopoiesis.
The following recipes are considered effective:
- Birch sap - drink 1 liter per day. If necessary, you can use tinctures from birch leaves or buds.
- Hawthorn - infused in cognac. The tincture is made at the rate of 70 g. hawthorn buds per ½ alcoholic beverage. The composition is left for 2 weeks. Take 1 tbsp. l. before every meal.
- Lingonberry - tinctures from leaves and berries have a positive effect. Lingonberry leaves are poured with boiling water and infused like tea.
Lingonberry decoction is taken after every meal. Fresh or soaked lingonberries are consumed on an empty stomach or before bed.
Alternative treatment does not replace traditional methods of therapy and the need to consult a doctor.
Changes that occur due to hypoxia are usually irreversible, so it is unacceptable to ignore this condition.
Hypoxia of the brain, heart, and kidneys is especially dangerous, since these systems are most sensitive to oxygen limitation.
What is hypoxia
In terms of the volume of blood flow serving the brain, the brain ranks first: 20% of the blood volume is spent on delivering oxygen and nutrients to the brain.
Brain tissue is extremely sensitive to a lack of oxygen: after 4 seconds of acute insufficiency, its functionality is impaired, after 8–12 seconds a person loses consciousness, and after 30 seconds a coma sets in. In the absence of blood flow, the brain is able to function for no more than 4–5 minutes.
In practice, the time interval is somewhat longer, since acute hypoxia associated with the complete disappearance of blood flow is a rare phenomenon. Most often, a person is faced with a decrease in oxygen in the blood or disturbances in the absorption mechanism. The prognosis for life in this case is better, but the consequences of hypoxia range from treatable to severe irreversible.
Types of pathological condition
Hypoxia is not an independent disease. This is a condition that occurs when the volume of oxygen entering the cells decreases. Many different factors lead to this.
Types by etiology
In relation to external factors, the condition is classified as follows.
- Hypoxic - or exogenous. The condition develops due to a lack of oxygen in the inhaled air. The most trivial reason is a poorly ventilated room, ineffective ventilation in a completely enclosed room. Climbers encounter this kind of condition when climbing, since the volume of oxygen in the air decreases with altitude.
- Respiratory - or breathing. Here, disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory tract are observed: pneumonia, exacerbation of bronchial asthma, dysfunction of the respiratory center, injuries, and so on. The reasons here are obvious and all efforts are aimed at treating the primary disease.
- Cardiovascular - or circulatory. The cause is changes in the composition of the blood that disrupt the normal flow of blood. This condition occurs with heart failure, narrowing of the working bed of the vessel due to thrombosis, atherosclerotic plaque, and so on. The consequences of hypoxia here are much more serious, including ischemic stroke of the brain.
- Hemic – associated with changes in blood composition. In the human body, oxygen molecules are transported in the form of a complex with hemoglobin. When the amount of hemoglobin or red blood cells decreases, oxygen remains unbound and, accordingly, cannot be delivered to the cell. The same picture is observed when the mechanism of binding hemoglobin with oxygen is destroyed.
- Tissue - in this case, the mechanism of oxygen utilization in the cell is disrupted, for example, when a fragment of the mitochondrial respiratory chain is blocked. Some poisons and medications have this effect.
- Overload is usually a temporary phenomenon associated with excessive stress on muscles, nerve tissue or organ.
- Technogenic - such hypoxia is formed due to the constant action of harmful, toxic substances in some industries.
- Mixed - any type of hypoxia, extended in time enough to cause tissue hypoxia. Here we need treatment of both the primary form and the secondary one.
Varieties by development time
Since hypoxia is a condition and not a disease, the rate of its formation can be very different.
- Lightning - for example, due to hemorrhage in the respiratory center or as a result of injury. If urgent assistance is not provided, this condition ends in death.
- Acute cerebral hypoxia develops over several hours. An example of this is cyanide poisoning, which blocks an enzyme in the respiratory chain. Help here is needed immediately, otherwise neither life nor health of a person is guaranteed. However, more time is allocated for treatment activities.
- Chronic brain hypoxia is not so life-threatening, but significantly reduces its quality. To compensate for the constant lack of oxygen, the body uses a variety of additional mechanisms. However, any of them are aimed only at maintaining vital functions, but not at all at fully restoring functions.
The most obvious compensation mechanisms include increasing the depth and frequency of inputs. Reserve alveoli begin to participate in breathing in order to maximize the working surface. Outwardly, this manifests itself as severe shortness of breath, which noticeably limits mobility. This increases the heart rate and blood pressure.
A redistribution of blood flow occurs: more blood is sent to the internal organs, and the periphery begins to experience secondary oxygen starvation. Lack of oxygen creates the need to increase the number of red blood cells, which significantly increases the risk of blood clots.
All this leads to rapid wear and damage to the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Therefore, treatment of hypoxia should be started at the earliest stages. Later, coping with the painful condition and the consequences of its compensation is much more difficult.
Classification by localization
A lack of oxygen can be observed in a specific area of the brain, or it can cover the entire organ.
The following types are considered:
- Scattered is a consequence of a general lack of oxygen in the blood. Causes low to moderate impairment. Curable with the most favorable prognosis.
- Central cerebral ischemia occurs when the blood supply to some part of the brain is disrupted. The cause, as a rule, is a narrowing of the vessel - an aneurysm, a blood clot. This condition is usually part of a larger medical condition.
- Global cerebral ischemia is a complete cessation of blood flow.
- Ischemic stroke – also caused by a sharp narrowing or obstruction of a blood vessel. Typically, a stroke affects several areas.
Symptoms of hypoxia
Like many other disorders in the central nervous system, hypoxia is accompanied by a deterioration in mental activity. The first signs of it are difficulties in solving problems, deterioration of short-term memory, that is, symptoms that can easily be attributed to fatigue.
At the next stage of acute hypoxia, the victim often experiences a state of euphoria. Excessive energy and excitement is accompanied by a clear lack of coordination and an unsteady gait.
Despite self-awareness from an objective point of view, cognitive functions deteriorate. Excitement is accompanied by pallor, but can sometimes cause redness of the skin. Profuse and unpleasant sweating, breathing and rapid heartbeat appear.
Excitement gives way to apathy, drowsiness, and is accompanied by dizziness. Vision decreases, spots appear before the eyes, then the patient loses consciousness. Fainting turns into a coma of varying depths.
Even at this stage, resuscitation helps not only save the patient’s life, but also completely restore all brain functions. Restoration occurs in reverse order.
The cause of chronic lack of oxygen is diseases associated with narrowing of blood vessels, for example: cervical artery syndrome with osteochondrosis, hypertensive encephalopathy, etc.
Symptoms of brain hypoxia include the following disorders:
- dizziness, constant ringing in the ears;
- constant headache. The pain is relieved with vasodilator drugs, but immediately returns;
- impaired balance, coordination, speech;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting in the morning;
- deterioration of mental abilities - memory impairment, decreased performance;
- various sleep disorders are possible;
- There is a sharp change in mood, tearfulness and irritability prevail, depression and apathy develop.
Treatment of chronic hypoxia is inseparable from the treatment of the underlying disease. Only by eliminating the primary factor can success be achieved by restoring normal blood supply to the brain.
Diagnostics
Acute hypoxia has quite characteristic symptoms, which facilitates diagnosis. The signs of chronic disease coincide with most of the symptoms of disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system, and in most cases the cause of their appearance is a lack of oxygen.
The goal of diagnostics for hypoxia is to establish the primary cause of the pathological condition.
- Blood test - both general and gas. The former indicates the number of red blood cells, the latter allows you to accurately determine the partial pressure of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
- An encephalogram of the head provides information about the state of brain cells and the presence of poorly functioning areas.
- Rheovasography allows you to determine the condition of the blood vessels supplying the brain.
- Angiography - general or selective, provides a more complete picture of blood flow.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is the most informational method. Indispensable for suspected ischemia of certain areas of the brain.
- Capnography and CO-metry indicate the volume of carbon dioxide in exhaled air. In this way, disturbances in lung function are excluded or confirmed.
Treatment
Since the causes of the condition are varied, different methods are used to treat cerebral hypoxia.
- The exogenous form requires only restoration of the normal oxygen content in the blood, and the source is inhaled air. The treatment method is an oxygen cushion.
- In case of respiratory hypoxia, treatment is aimed at restoring the functions of the respiratory tract. For this purpose, respiratory analeptics, drugs that dilate the bronchi, and antihypoxanes are used.
- In the hemic form, drugs are used to help restore hematopoietic function. A common method is blood transfusion.
- To treat circulatory hypoxia, anticoagulants, vasodilators, nootropics, decongestants, angioprotectors, and so on are prescribed.
- The tissue form involves the use of antidotes if the root cause is poisoning. Any measures aimed at improving oxygen supply are acceptable: taking vitamins, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and even walking in the fresh air.
Acute cerebral hypoxia is a fatal condition. Chronic significantly reduces the standard of living. Any form of the disease requires effective and immediate treatment.
My grandmother developed hypoxia after a stroke. She underwent a long rehabilitation: she took Divaza and went to exercise therapy. Now, thank God, everything is back to normal.
- Diseases
- Body parts
A subject index to common diseases of the cardiovascular system will help you quickly find the material you need.
Select the body part you are interested in, the system will show materials related to it.
© Prososud.ru Contacts:
Use of site materials is possible only if there is an active link to the source.
Diagnosis of cerebral hypoxia - the dangers of oxygen deprivation
Lack of oxygen entering the brain causes pathological disorders and coma. The most serious consequence is death. Severe cerebral hypoxia leads to death in just a few minutes.
Brain hypoxia - what is it?
In simple terms, hypoxia is oxygen starvation. The human brain has a large number of blood vessels that supply various sections with nutrients. Brain tissue is sensitive to loss of oxygen.
- Lightning oxygen starvation - develops quickly, lasting only a few minutes or seconds.
The negative effect of hypoxia on the brain is tissue death and loss of functionality. The consequences of oxygen starvation depend on the duration of the disorders, as well as the complications caused by them.
Causes of oxygen starvation of the brain
Symptoms of brain hypoxia depend on the causes of oxygen starvation. The etiology of disorders includes several main factors that provoke pathological changes:
- Exogenous - occurs due to low oxygen content in the air. Occurs when rising to a height, staying in a closed room for a long time, or low air pressure.
How does a lack of oxygen manifest itself in the brain?
Symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain make it possible to accurately determine the presence of disorders. The attending physician will pay attention to the following deviations:
- Stage of increased excitability - moderate post-hypoxic changes in brain structures lead to a state of euphoria, the ability to fully control one’s actions and movements is lost.
A symptom of the brain’s attempts to correct disturbances is the appearance of cold sweat and perspiration.
At the same time, there is a violation of visual functions: clarity of vision, darkening of the eyes. The development of oxygen starvation leads to loss of consciousness.
With increased sensitivity of the brain to hypoxia, the condition is accompanied by coma.
Why is brain hypoxia dangerous?
Oxygen starvation is a dangerous condition that leads to pathological changes that affect brain activity, as well as disruption of its basic functions. The prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of damage and the time during which hypoxia was observed.
Consequences in adults are associated with the difficulty of restoring even minimal motor and speech functions. Prolonged oxygen starvation leads to coma and death.
Post-hypoxic brain changes
The consequences of brain hypoxia after clinical death include loss of neurological functions. After the patient returns to life, the doctor’s task is to determine the presence of irreversible changes.
- Complete restoration of brain function – rapid or delayed recovery of functions is observed. Normalization of the condition occurs within several days or months. Possible deterioration in health.
Interrupted recovery is also diagnosed, in which a rapid improvement in well-being occurs. In this case, after several weeks or months, secondary deterioration occurs, transforming into persistent neurological dysfunction.
Treatment of cerebral hypoxia is fraught with difficulties. Full recovery is extremely rare, but with proper therapy, stable remission can be achieved.
Does the brain recover after hypoxia?
Brain cells do not recover after hypoxia. But with properly prescribed therapy, it is possible to provide the proper conditions for normalizing the daily functions of the body.
Brain hypoxia in newborns
The share of congenital pathologies and hypoxia accounts for about 30-35%. This pathology occurs due to oxygen starvation of the fetus during development in the womb. Lack of oxygen in the brain in a newborn leads to abnormalities in the development of internal organs: lungs, liver, cardiovascular and central nervous systems.
What causes a baby's brain to lack oxygen?
As already noted, it is the blood that supplies oxygen to the brain. Responsible for transporting the nutrient element - hemoglobin. To create a sufficient amount of this substance, a large amount of iron elements is required.
The diagnosis of fetal hypoxia is made in approximately 10-15% of pregnancies. The doctor delivering the baby will pay attention to the condition of the newborn. The prerequisites for cardiac monitoring and additional examination are:
- Turbid waters with a greenish tint.
Signs of post-hypoxic changes in the brain in a newborn manifest themselves in characteristic symptoms: neurological seizures, disruption of life rhythms, irritability and tearfulness. In combination with the results of ultrasound of the newborn’s brain and medical history, an accurate diagnosis of the presence of oxygen starvation can be made.
What consequences can hypoxia cause in an infant?
The consequences of neonatal hypoxia depend on the degree of damage and the presence of irreversible changes in the central nervous system. With mild damage, complications manifest themselves in the development of perinatal encephalopathy.
What and how can you treat hypoxia?
The main task of medical personnel is to restore normal oxygen supply to the brain, as well as stabilize the patient’s condition. To provide proper treatment, it is necessary to recognize disorders, provide first aid and prescribe adequate therapy.
How to determine hypoxia
Medical personnel have various research methods at their disposal that make it possible to diagnose disorders even at an early stage.
- Ultrasound - echography of hypoxic changes - is a fairly reliable method, widely used to diagnose deviations from the norm during the intrauterine development of a child. The method allows you to determine oxygen starvation even at an early stage.
Echographic signs of hypoxic brain damage indicate the total volume of necrotic phenomena in adults, and make it possible to make an approximate prognosis of the development of the disease.
First aid for lack of oxygen in the brain
Oxygen starvation manifests itself in fainting and loss of consciousness. When the first symptoms of disorders appear, it is necessary to provide the patient with unhindered access to fresh air.
Medicines for oxygen starvation of the brain
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the causes of hypoxia. In any case, iron supplements and a vitamin complex are prescribed, which improve tissue metabolism and hematopoiesis.
Along with drug treatment, blood transfusions and artificial ventilation are used. In some cases, surgery is indicated.
Breathing exercises for hypoxia
One of the most effective means of increasing the brain’s resistance to hypoxia is the use of breathing exercises. Several types of different techniques have been developed aimed at combating pathological abnormalities.
Folk remedies for hypoxia
Folk remedies are aimed at saturating the cerebral cortex affected by hypoxia with nutrients by improving metabolism and hematopoiesis.
- Birch sap - drink 1 liter per day. If necessary, you can use tinctures from birch leaves or buds.
Lingonberry decoction is taken after every meal. Fresh or soaked lingonberries are consumed on an empty stomach or before bed.
Alternative treatment does not replace traditional methods of therapy and the need to consult a doctor.
What causes a subependymal brain cyst in newborns, consequences and removal
Is a cerebral pseudocyst dangerous in a newborn and how to get rid of it?
Symptoms and treatment of cysts of the transparent septum of the brain
Causes of cerebral gliosis, likely consequences, treatment
What are cystic-gliotic changes in the brain, why is it dangerous?
What causes brain atrophy, how to deal with tissue transformation
Oxygen starvation of the brain: symptoms and treatment
Hypoxia, or in simple terms - oxygen starvation of the brain, is a serious disease that requires diagnosis and treatment. Hypoxia blocks the flow of oxygen to nerve connections. In the case where there are no symptoms of dysfunction, the brain can withstand 4 seconds of acute hypoxia; just a few seconds after the cessation of blood supply, the person loses consciousness; after 30 seconds, the person falls into a coma.
The most serious outcome of this violation is the death of a person. Therefore, it is important to know the main causes of oxygen starvation of the brain and the symptoms that will help to identify the first signs of the disorder and avoid serious consequences and long-term treatment.
There are 3 types of hypoxia:
- Fulminant hypoxia – development occurs quickly, within a few seconds and minutes;
- Acute hypoxia - lasts for several hours, the cause may be a heart attack, poisoning;
- Chronic insufficiency - develops over a long time, the causes are heart failure, cerebral atherosclerosis, heart disease.
Causes of oxygen starvation
Oxygen deficiency in the brain can be caused by several reasons:
- Respiratory – the brain is not able to receive the proper amount of oxygen due to impaired respiratory processes. Examples include diseases such as pneumonia, bronchial asthma, and chest trauma.
- Cardiovascular – a violation of blood circulation in the brain. Causes may include: shock, thrombosis. Normalizing the functioning of the heart and blood vessels helps prevent the development of cerebral stroke.
- Hypoxic – oxygen starvation, which occurs when oxygen in the air decreases. The most striking example is climbers who, when climbing a mountain, most clearly feel the lack of oxygen.
- Blood – with this factor, oxygen transport is disrupted. The main reason is anemia.
- Tissue – development occurs due to disruption of oxygen transport. The cause may be poisons or medications that could destroy or block enzyme systems.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of lack of oxygen in the brain may manifest differently in each person. In one patient, sensitivity may decrease, lethargy may appear, and in another, headaches may begin.
The main symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain:
- Dizziness, the possibility of loss of consciousness due to inhibition of the activity of the nervous system. The patient experiences severe attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- Visual impairment, darkness in the eyes.
- Change in skin color. The skin turns pale or red. The brain reacts and tries to restore blood flow, resulting in cold sweat.
- Adrenaline increases, after which muscle weakness and lethargy occurs in the patient. A person ceases to control his movements and actions.
- Irritability, resentment appear, depression and other mental disorders develop.
- Inattention, the patient has difficulty absorbing information, mental performance decreases.
The final stage of the disease with oxygen starvation is the development of coma, and then soon respiratory and cardiac arrest.
If the patient receives timely medical care, all body functions can be restored.
Diagnosis and treatment
To determine the patient's current condition and whether he is truly sick, a number of medical tests are required.
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. This method shows the consequences of oxygen deficiency. With this method, you can see areas of the brain where sufficiently saturated oxygen enters.
- Ultrasound is a method that allows you to determine deviations from the norm during the development of a child in the womb. Allows you to determine oxygen starvation at the initial stage.
- Complete blood count and clinical tests for acid-base balance.
- General and selective angiography.
Treatment of oxygen deficiency primarily involves restoring the required supply of oxygen to the brain.
If there is a lack of oxygen in the brain, the following measures are prescribed:
- Maintaining normal functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- Drugs to improve blood circulation in the brain;
- Antihypoxanes;
- Decongestants;
- Bronchodilators.
Radical treatment of the disease is also carried out when the patient is already in serious condition. This treatment includes: blood transfusion, installation of an oxygen mask, procedures for resuscitation of the patient.
Prevention of hypoxia
Preventing a disease is always easier than treating it. For normal oxygen intake into the body, you just need to follow the recommendations of specialists. These tips can be used both for the prevention and treatment of oxygen deficiency.
Key tips include:
- Fresh air. Walks should take at least 2 hours, preferably before bedtime. It is better to take walks in environmentally friendly places (parks, forests).
- Sport. Light exercise in the morning promotes better blood circulation, and if you do it outside, the effect will be doubled.
- Correct daily routine. You need to normalize your routine, allocate the required time for rest and sleep. To normalize processes in the body, you need to devote at least 7-8 hours to sleep. Don't forget to warm up if you work at a desk.
- Proper nutrition. For the normal supply of oxygen to the brain, nutrition plays an important role. The diet should consist of a large number of vegetables and fruits. You should eat foods rich in iron (buckwheat, meat, dried fruits), while dairy products and coffee consumption should be kept to a minimum.
- No stress. Try to avoid stressful situations and not get nervous in vain.
Respiratory prevention of oxygen deficiency
One of the most convenient and simplest ways to prevent disease is breathing exercises. This method is very easy to use and does not require any additional effort.
A few useful exercises to take note:
- Relax completely, take a 4-second deep breath, then hold your breath for the same time and exhale slowly. Repeat about once. After 1 month, increase the time of inhalation and exhalation.
- Take a deep breath and take at least 6-7 short exhalations through your nose. The mouth remains closed. Repeat 3-4 times.
It is advisable to repeat these exercises 2 to 4 times a day.
Oxygen starvation in newborns
Symptoms of lack of oxygen in the brain can appear in a newborn during the period when the baby is still in the womb, or immediately during childbirth. Hypoxia in a severe stage, not rarely, can lead to serious consequences for both mother and baby.
Of these we can note:
Reasons why these severe consequences may occur in children:
- Problems of the cardiovascular system;
- Intrauterine infections;
- Improper lifestyle (alcohol, cigarettes, drugs);
- Fetal pathology;
- Birth injuries.
Oxygen deficiency, as a diagnosis, is made in approximately 15% of pregnancies.
Most often, brain hypoxia in a child develops due to the mother’s poor lifestyle, drinking alcohol, and smoking.
Therefore, in order for your child to grow up as a healthy and strong child, you should give up bad habits.
Danger of brain hypoxia
A state of oxygen starvation can lead to pathological changes. Brain activity and basic brain functions are impaired.
Whether the prognosis is favorable depends on the degree of brain damage and at what stage the disease was discovered.
A person's chances of recovery also depend on his current condition. With a prolonged coma, the basic functions of the body are impaired and the chance of recovery becomes very low.
With a short-term coma, the chances of rehabilitation are very high. However, treatment may take quite some time.
Video
In general, the symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain can be supplemented, depending on the type of hypoxia. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor, because only he, based on the results of examinations, will be able to determine what caused the malfunction in the body and what measures should be taken.
Lack of oxygen in the brain treatment
in DiseasesViews
Doctors call oxygen starvation of the brain hypoxia. This condition occurs as a result of insufficient oxygen supply to the human body. Also, the cause may be various disruptions in its functioning - there are situations when cells fail to absorb oxygen. In any case, the body's cells do not receive enough oxygen.
Symptoms
The first symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain must be responded to immediately. Signs of starvation of the human brain from oxygen deficiency in the first stages may be almost imperceptible, but subsequently can cause irreparable damage to the entire body.
- A person experiences a sharp excitement in the body, an increase in adrenaline and a state of euphoria. Then, this state quickly turns into lethargy, lethargy and fatigue. After a surge of strength, people feel very tired and apathetic. In this state, you feel very dizzy, your heart rate increases, cold sweat appears, and convulsions may occur.
- Sudden deterioration of memory, a person may not be able to navigate his location and suddenly forget where he was going and what he wanted to do. People experience confusion and even disorientation. This condition quickly passes, having calmed down, people do not pay much attention to it, attributing their condition to fatigue, overwork or prolonged fasting.
- A symptom of hypoxia can be caused by a sharp headache. This occurs due to pressure differences and a long stay in a stuffy room.
- Loss of sensitivity in various parts of the body. An arm or leg may not obey, or involuntarily perform uncontrollable actions. After recovery, people experience feelings of lethargy and pain in their limbs.
- Nervousness increases sharply. A person wants to cry or laugh for no apparent reason.
- Symptoms of brain oxygen deficiency include sleep disturbance. People suffer from insomnia. They often wake up in the middle of the night and cannot sleep for a long time.
- General fatigue of the body. The person feels overwhelmed and cannot concentrate on certain work. Irritability and aggression appear.
- Violation of visual and speech functions of the body. People cannot pronounce a few words coherently.
Oxygen starvation of the brain can be caused by a long stay at great depths, being at a height, being in a very polluted room, a severe lack of oxygen or asphyxia, or being in a stuffy room for a long time.
All symptoms indicate a sharp deterioration in brain performance and can lead to serious disruptions in the functioning of the entire human body. It is necessary to pay attention to the symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain and immediately contact a specialist. Early diagnosis and timely treatment will prevent deeper diseases.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage in newborns here
In this article you will learn what are the causes of cerebral encephalitis http://golovnojmozg.com/bolzn/entsfl/ents-golovnogo-mozga.html
Causes
The reasons for oxygen starvation of the body are different. This condition may occur:
- when the volume of oxygen in the air that a person inhales decreases (this phenomenon is observed when climbing mountains or when staying in poorly ventilated rooms);
- when there is a mechanical obstruction to the flow of air into a person’s lungs (observed when the airways are closed with water or vomit, or when the nasal passages are narrowed as a result of an allergic reaction);
- in case of carbon monoxide poisoning;
- with large blood loss;
- when taking certain medications;
- with a lack of vitamin B2 as a result of liver cirrhosis or hepatitis.
In addition, a condition in which oxygen starvation of the brain and heart occurs is caused by coronary artery disease, thrombosis, vascular spasms and smoking.
Treatment
In any case, a person suffering from oxygen starvation of the brain needs emergency help. When the first symptoms appear, you must immediately call a doctor, and before his arrival, provide the patient with an influx of fresh air. You need to unfasten tight clothes, perform artificial respiration, pour water out of your lungs, and take them out of the smoky room into fresh air.
Doctors then ensure that the body is oxygenated. In particularly severe situations, a blood transfusion may be necessary. If necessary, a person is prescribed decongestants, as well as various therapeutic procedures. To treat hypoxia in newborns, they are placed in a special chamber, resuscitation measures are carried out, and nutrient solutions are administered.
Consequences
The brain cannot tell the heart to beat faster or slower. The functioning of the heart is controlled by the cells of the body's tissues. Oxygen serves as a tool for controlling heart pulsation. When there is a lack of oxygen, cells require blood saturated with it. The heart speeds up its work and muscle tension. This increases the speed of blood flow and blood pressure.
As soon as the required amount of oxygen arrives, the cells relieve their demands, and the heart switches to a calm mode of operation, the pain subsides. Only daily gymnastics, feasible physical work and proper nutrition can ensure good capillary permeability. A person should spend 1/10 of his daily time to ensure good health.
When you inhale, air enters the lungs and expands the alveoli. If the inhalation is weak, then a small part of the alveoli moves apart, and not the entire surface of the blood vessels comes into contact with the incoming air. In this case, the lungs will not provide the body's need for oxygen.
With a large, energetic inhalation, the alveoli will be pressed against each other, the blood vessels will be compressed, their area in contact with the air will decrease, and the movement of blood in them will slow down. Blood oxygen saturation will be low - acute oxygen starvation will occur. The person may become dizzy and lose consciousness. You need a comfortable, free breath that fills the lungs completely.
Weak inhalation and excessive filling of the lungs with air cause unsatisfactory oxygen saturation of the blood.
Everyday breathing is breathing in which a constant sequence of inhalation, exhalation and pause is observed. This is common, a person breathes this way from birth to death, but the body’s need for oxygen is not always met.
Oxygen starvation of the body occurs when the oxygen content in the inhaled air decreases, the body is in a painful state, metabolism in cells is activated, heavy physical work is performed, nervous overexertion, food consumption is excessive and the body is aging. A person does not immediately feel oxygen starvation. He does not pay attention to discomfort in the body, malaise, changes in blood pressure and pulse, profuse sweating, unexpected pain in the heart and head, etc.
With temporary oxygen starvation, blood pressure changes, arrhythmia, headaches and heart pain occur, vision and hearing deteriorate, and the body’s self-defense functions decrease.
With prolonged oxygen starvation, in addition to the symptoms of temporary oxygen starvation, diseases arise:
- heart, circulatory system (angina pectoris, heart failure, heart attack, varicose veins), brain (stroke), etc.;
- metabolism in cells - obesity, diabetes, liver disease, etc.;
- body defense systems (tumors of various etiologies).
Prolonged oxygen deprivation suppresses the body's ability to heal itself.