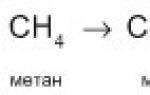
What does it mean to contain vegetable oils? Types of vegetable oils, classification and application
The benefits of vegetable oil
Fats play an important role in the life of the body; they are the main structural components of cell membranes, serve as the main source of energy, form a reserve of energy material, and protect internal organs from hypothermia. When the body is dehydrated, adipose tissue serves as an internal source of water.
Natural, unrefined, cold-pressed vegetable oil has unique beneficial properties. Cold-pressed vegetable oils retain all valuable biologically active substances: polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acids. Vegetable oil is used not only for food and cosmetic purposes, but also for the treatment and prevention of various diseases.
Vegetable oil enriches our diet with valuable unsaturated fatty acids, which cannot be synthesized in our body, without which the formation of new cells and the normal functioning of the nervous, immune, reproductive and cardiovascular systems are impossible. Many vegetable oils are rich in tocopherols (vitamin E) - natural antioxidants that participate in the processes of cell renewal and regeneration, heal and rejuvenate the body.
Vegetable oil supplies us with energy, nourishes brain cells, maintains the strength and elasticity of blood vessels, improves blood composition, prevents the formation of blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques, prevents the development of cancer cells, activates smooth muscle fibers and protects the gastric mucosa, stimulates the formation and secretion of bile, improves hormonal background, reduces inflammation, cleanses the body of waste and toxins, relieves constipation, improves skin condition, strengthens teeth, hair and nails.
Of particular value is polyunsaturated linolenic acid Omega-3, which enters our body less and less with food. Most people's diet consists of saturated fatty acids, which raise blood cholesterol levels. Consumption of linolenic acid has a positive effect on human health. Omega-3 has a beneficial effect on atherosclerosis, type 2 diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, obesity, chronic allergic and inflammatory diseases, Alzheimer's disease, reduces the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, certain cancers, and prevents the development of cardiac arrhythmias and dysbiosis. Essential linolenic acid is necessary for the growth and proper development of the brain in children, the organ of vision, gonads, kidneys, skin, hair and nails.
On many sites you often find information that oils contain many vitamins and minerals, but this is not true, since oil is a fat and the main value in it is unsaturated fatty acids. Do not confuse oil and the crops from which the oil is extracted. The main vitamin contained in some oils is vitamin E; other vitamins may be present, but in very small quantities.
Comparative table of vegetable oils by Omega-3, Omega-6, Omega-9 and vitamin E content per 100 g of oil
| Vitamin E | mg | Omega-3 | % | Omega-6 | % | Omega-9 | % |
| Cedar oil | 55 | Linseed oil | 53.3 | Grapeseed oil | 69.6 | Sunflower oil | 82.6 |
| Sunflower oil | 41.08 | Camelina oil | 38 | Milk thistle oil | 62 | Olive oil | 71.2 |
| Camelina oil | 40 | Hemp oil | 21.5 | Walnut oil | 52.9 | Almond oil | 69.4 |
| Almond oil | 39.2 | Pumpkin oil | 14 | Cedar oil | 46.2 | Peanut butter | 44.8 |
| Grapeseed oil | 28.8 | Walnut oil | 10.4 | Black cumin oil | 42.7 | Sesame oil | 39.3 |
| Peanut butter | 15.6 | Mustard oil | 5.8 | Sesame oil | 41.3 | Cocoa butter | 32.6 |
| Olive oil | 14.35 | Soybean oil | 5.1 | Pumpkin oil | 39 | Pumpkin oil | 32 |
| Soybean oil | 8.18 | Black cumin oil | 1 | Peanut butter | 32 | Cedar oil | 25.2 |
Cold pressed vegetable oil
Production of healing vegetable oil
Natural vegetable oil is a chemically active substance that interacts with air, light and metal. During this interaction, many beneficial substances in the oil are destroyed. Ideally, extra virgin oil should not come into contact with metal; immediately after pressing, it should be placed in a glass container and protected from exposure to sunlight, otherwise it will become ordinary edible oil.
Press for cold pressing of oil oak



How to use vegetable oil
Vegetable oils are high in calories, so any vegetable oil should not be consumed in large quantities. 1-2 tablespoons of oil daily or several times a week is enough.
Most unrefined vegetable oils cannot be used for frying. For frying, use ghee and unrefined sunflower oil.
Why you can fry with cold-pressed sunflower oil
Where did the slogans come from that you can’t use cold-pressed sunflower oil for frying? After all, this is all an advertising campaign for refined sunflower oil! And all because it is much cheaper and faster to produce refined oil than unrefined oil. Think about it, because before there were no technologies for the production of refined oil, and our grandmothers used natural sunflower oil with a scent. And refined oil is a surrogate in which, after so many stages of processing, there is nothing left useful for the body. In addition, it is produced using petroleum products, which are not completely removed during oil purification, and we use them together with oil. Consuming refined sunflower oil is harmful to health!
If you want to fry something, use cold-pressed sunflower oil. The downside is that when heated, many useful substances are lost and some may not like the fact that the products are saturated with the smell of sunflower oil. But it is better to use unrefined oil than harmful refined oil.
Of course, the best oil for frying is ghee. You can also fry in coconut, olive, soybean, mustard oils. For example, Italians fry everything in cold-pressed olive oil. The main thing is not to heat the oil to 100 °C. It is enough to heat it until the first bubbles appear.
The three enemies of all vegetable oils are light, heat and air, which enhance the oxidation process, so do not store the oil on the windowsill, near the stove, or in an open bottle.
How to store vegetable oil
The three enemies of all vegetable oils are light, heat and air.
Try to buy vegetable oils in small glass bottles, since after opening and contact with air, the shelf life of the oils decreases. Cold pressed oil is recommended to be used within 1-4 months.
It is good to store oil in food-grade steel containers, since during such storage the oil is protected from light.
Introduce different oils into your diet so that you do not consume the same oil for a long time, but stick to a varied diet.
To get the maximum benefit from consuming vegetable oils, you should buy unrefined oils obtained by cold pressing. The maximum natural vitamins and microelements are contained only in cold-pressed oil.
The vitamins listed on the package in refined oil are of synthetic origin; they are enriched with oil that has already been purified of impurities.
Most unrefined vegetable oils are not intended for frying. Vegetable oil should be added to prepared dishes.
How to choose vegetable oil
When purchasing vegetable oil, read the label carefully.
First of all, when buying vegetable oil, pay attention to the shelf life of the oil - the shorter it is, the more natural the oil.
Manufacturers often write bombastic statements to advertise their product and attract the attention of buyers.
It’s good if the label has the “PCT” symbol or the phrase “Technical regulations for fat and oil products.” It’s even better if the oil is certified in accordance with the requirements of the international quality standard ISO 9001. This proves that the product has passed the certification procedure and meets safety and quality standards, including the content of pesticides, heavy metals and other environmental indicators. And the phrases “Natural”, “Increased environmental purity”, “Produced in an environmentally friendly way” and similar expressions do not mean anything. In our country, the law allows such statements to be written on the label.
The label may contain the currently popular phrase “Oil without preservatives and dyes.” Artificial colors or preservatives are usually not added to vegetable oils, since most of them are water soluble and do not mix with the oil. Therefore, this phrase applies to all oils and has no meaning. The same applies to B vitamins. They are water-soluble and cannot be contained in pure vegetable fat.
Very often, manufacturers write “Cholesterol Free” on the label. The fact is that there is no cholesterol in any vegetable oil, since this substance is synthesized only in the body of animals and humans. Therefore, this is another advertising ploy. Vegetable oil contains phytosterols.
Often on refined oil it is written that it contains fat-soluble vitamins A or E. This is pure deception, since refined oil does not contain natural fat-soluble vitamins - they, like most other useful substances, are removed during the refining process.
- The sediment formed during cold-pressed oil storage is not harmful to health and consists of minerals and phospholipids that are beneficial to the body.
- Vegetable oils that taste rancid are not suitable for consumption, with the exception of some naturally bitter oils such as olive or flaxseed. Oils that have undergone oxidation contain toxic compounds that can cause numerous diseases.
- Do not use oils that have expired.
- Since salt does not dissolve in vegetable oil, before seasoning a salad of fresh vegetables and herbs with oil, the dish is first salted, wait until the vegetables give juice, and only then add oil.
Contraindications
Despite the numerous beneficial properties, vegetable oils should be treated with caution by people with:
- stones in the bile ducts and gallbladder, since oils can cause stones to move forward and block the ducts;
- disorders of bile secretion;
- recent gallbladder removal;
- diarrhea of any origin, since oils have a laxative effect;
- hepatic cellular failure observed in cirrhosis and hepatitis.
However, even in these cases, you should not completely eliminate vegetable oil from your diet; you should just limit its daily consumption. A complete refusal of oils can cause serious hormonal disorders, nervous system disorders, hypovitaminosis and other malfunctions of the body.
Sunflower and olive, corn and peanut, sesame and pumpkin, mustard and hazelnut... How much do you know about these types of vegetable oil? And have you tried everything?
Until recently, I myself did not know about the existence of many oils, until my mother brought me peanut butter and pumpkin seed oil. She turned out to be right - it’s healthy and incredibly tasty!
A slender woman needs to know that frying in oil is harmful. When heated, many oils completely lose their healing properties, and some even become dangerous. They oxidize and release very harmful substances, which require a lot of energy to neutralize, which negatively affects the functioning of the liver. Oncologists have discovered that repeated heating of fat (for example, deep-frying, in a frying pan) leads to the formation of carcinogenic substances in the oil, which provoke the appearance of tumors in the body.
But adding vegetable oils to salads and ready-made dishes as a sauce or dressing is not only healthy, but also incredibly tasty! In this case, the oil retains all its unique properties, because each of them has its own characteristics, its own “zest”!
Vegetable oil is necessary for our body
 Oil is necessary for our body to function normally, as it contains various vitamins and essential fatty acids.
Oil is necessary for our body to function normally, as it contains various vitamins and essential fatty acids.
But this is not all the advantages of vegetable oils - it also strengthens the immune system and heals. Nutritionists advise eating up to 50 g of unsaturated fats daily: only then will our diet be balanced.
Each of the vegetable oils has its own unique characteristics, Therefore, by trying different varieties, you will make your dishes delicious and your nutrition healthy.
Some vegetable oils control cholesterol levels, while others are an excellent alternative to butter for home baking.
Cost of vegetable oils
Most of the oils are not cheap. The most inexpensive natural vegetable oils are sunflower, olive, grape seed oil, flaxseed and mustard. The most expensive ones are pine nut oil, almond oil, pistachio oil, and hazelnut oil. This oil is suitable as a gift for someone who cares about their health.
It is profitable to buy oil for 2. For example, my mother and I buy and divide by 2: you don’t overpay for a bottle.
| Sunflower oil “Homemade Ukrainian” | 0.5 liters | 147 |
| Flaxseed oil (Dial-Export) | 0.5 liters | 152 |
| Soybean oil | 0.5 liters | 175 |
| Corn oil | 0.5 liters | 269 |
| Mustard oil | 0.5 liters | 290 |
| Olitalia grape seed oil | 1 liter | 310 |
| Peanut butter (Dial-Export) | 0.5 liters | 360 |
| Walnut oil "Beaufor" | 0.5 liters | 385 |
| Hazelnut oil "Beaufor" | 0.5 liters | 430 |
| Pumpkin seed oil "Pelzmann" | 0.5 liters | 415 |
| Almond oil "Beaufor" | 0.5 liters | 530 |
| Pistachio oil "Beaufor" | 0.5 liters | 670 |
| Cedar oil (Dial-Export) | 0.5 liters | 1200 |
Vegetable oils and their properties (benefits)
 |
Sunflower oilThe main source of vitamin E, which protects against atherosclerosis. Contains vitamin F, essential for cells liver, blood vessels and nerve fibers. Great for frying, stewing, salad dressing. |
Olive oilImproves heart function. The highest quality oil is first pressed (or cold pressed). Suitable for quick cooking and salad dressing. The ideal temperature for frying is 180 °C. |
 |
 |
Pumpkin seed vegetable oilIncreases good cholesterol levels rich in zinc, which stimulates the immune system. Suitable for seasoning snacks and meat, but it is better to do this at the end of cooking, the oil does not withstand heat. |
Coconut vegetable oilThis oil is rich in lauric acid, which enhances metabolism. It is 90% saturated fat and very high in calories. Retains its properties even at very high temperatures. Ideal for baking. |
 |
 |
Peanut vegetable oilReduces bad cholesterol levels. Due to its excellent heat-resistant properties and delicate aroma, refined oil is recommended for deep-fried cooking. |
Flaxseed vegetable oilOne of the richest sources of omega-3 fatty acids(60%), which protect the heart and blood vessels, improves kidney function, and helps get rid of constipation. Used for making sauces and salad dressings. |
 |
 |
Rice oilRice bran oil contains unsaturated fatty acids, vitamins (A, PP, E, B) and antioxidants: gamma-oryzanol, squalene (necessary for normal skin functioning) and ferulic acid. Its use contributes to more effectively lowering cholesterol levels in blood plasma compared to other vegetable oils. Withstands temperatures up to 254 °C. Makes food less fatty. |
Sesame oil |
 |
 |
Truffle oilIt is obtained not by pressing, but infusing truffles in olive or grape oil. This oil is used to flavor dishes when preparing pasta or risotto. Does not withstand heat treatment. |
Walnut oilContains vitamins A, E, C, B, macro- and microelements (zinc, copper, iodine, calcium, magnesium, iron, phosphorus). Necessary for elderly people. Indispensable for marinades, salad dressings, and fish. |
 |
 |
Cedar oilRich in fatty acids vitamins, macro- and microelements. Indispensable for tuberculosis, atherosclerosis, hypertension, stomach problems. Recommended as a dressing for dishes. |
Grape seed oilRich in vitamins, microelements, tannins. Prevents the development of atherosclerosis. Withstands high temperatures without changing taste and smell. An excellent addition to salads and marinades. |
|
 |
Soybean vegetable oilThis valuable edible oil is the record holder among vegetable oils for the content of beneficial microelements. Soybean is the only plant that can replace animal proteins. Used for salads, cold vegetable and meat dishes, dishes with potatoes. Meat and fish fried in soybean oil turn out to be very tasty and juicy. A valuable component extracted from soybean seeds along with fatty oil is lecithin. It is the main nutrition of the entire nervous system, is the most important building material for the brain, reduces cholesterol levels and the concentration of fatty acids in the blood, improves liver and kidney function. |
Mustard vegetable oilSeveral centuries ago, mustard oil could only be tasted at the royal court, in those days it was called an “imperial delicacy.” Mustard oil contains absolutely all fat-soluble vitamins, it has a specific aroma and piquant taste, is perfect for dressing salads, and emphasizes the taste of vegetables. In addition, salads with this dressing stay fresh longer. Any baked goods that contain this product turn out fluffy and do not go stale for a long time. |
 |
 |
Corn vegetable oilThis oil is made using a special vitamin-preserving technology from corn germ. Ideal for frying, stewing meat, fish and vegetables, baking, salad dressing and canning. Corn oil is considered a dietary product and is ideal for baby food. This oil is rich in vitamins E, B1, B2, PP, K3, provitamins A. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (OMEGA-6 and OMEGA-3) contained in corn oil increase the body's resistance to infectious diseases and facilitate the removal of excess cholesterol from the body. The amount of vitamin E in corn oil is almost 2 times higher than olive oil. Corn oil helps eliminate fermentation processes in the intestines, reduces cholesterol levels in the blood, relaxes the tone of the smooth muscles of the gallbladder, stimulates the secretion of bile, has an antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory effect, and improves brain function. |
Hazelnut vegetable oilThe oil was first obtained in France, a country of gourmets; since then it has begun to gain fame and popularity in other countries and even on other continents. We can talk continuously about how beneficial hazelnut oil is for a very long time. This vitamin helps prevent heart disease and cancer.. It supports the immune system and is involved in the important process of repairing human DNA. Therefore, it is useful to use hazelnut oil as a preventive measure if you are predisposed to such diseases. The oil will add a refined taste to any dish. Using oil will give baked goods a light nutty aroma and a delicate taste, and if you season fish with it, its taste will be simply unforgettable. Hazelnut oil is used to season ready-made dishes, thus preserving its beneficial properties. |
 |
 |
Pistachio oilPistachio oil- This is an excellent nutrient for significant physical and mental stress and after serious illnesses. Due to their high nutritional value and value, they are used in the nutrition of malnourished patients. Amazingly tasty, tender green kernels have a beneficial effect on brain function; when consumed regularly, they reduce susceptibility to heart disease, remarkably tone and improve mood. Useful for decreased liver function, opens blockages in the liver, helps in the treatment of jaundice, as a pain reliever for hepatic and gastric colitis. Used to treat anemia, useful for chest diseases, coughs, and used as an anti-tuberculosis agent. They have an invigorating, tonic and general strengthening effect. Useful for people suffering from arterial hypertension, chronic anemia, tuberculosis, thrombophlebitis. The property of pistachios to increase potency has been described. |
Walnut oilIt has immunomodulatory, bactericidal, antitumor, regenerating properties. It is consumed in prophylactic doses, usually in small quantities (from a few drops for children to a teaspoon for adults) before meals. The healing effect of the oil It also manifests itself in cases where eating nuts directly is contraindicated. For example, if you have colds, bronchitis, or some stomach diseases, you should not eat nuts. But oil is not only possible, but necessary! It is used in cooking, for preventive purposes, medicinal purposes and even for cosmetic purposes. |
 |
 |
Australian Macadamia Nut OilMacadamia nut oil They are used as food for preparing hot dishes, for frying and for dressing salads. They also consume 1 tablespoon per day on an empty stomach as a source of fat, for sore throats, headaches, migraines, arthritis and an increased susceptibility to tumor diseases. Macadamia– a storehouse of valuable nutrients. This nut helps remove cholesterol from the body and is a source of calcium and other minerals. It is low in carbohydrates, but relatively high in fat. According to scientists, regular consumption of oil from these nuts reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases, some types of cancer, and even promotes weight loss. |
 All oils have their own alluring aroma. Any bread with peanut butter will be magical, any salads and vegetables with pumpkin seed or pine nut butter will become piquant. The ideal option is to steam it and then sprinkle the food with oil.
All oils have their own alluring aroma. Any bread with peanut butter will be magical, any salads and vegetables with pumpkin seed or pine nut butter will become piquant. The ideal option is to steam it and then sprinkle the food with oil.
Vegetable oils can be bought at a large supermarket or online store. I'm looking forward to trying hazelnut and pistachio butter and I wish you the same!
Many will object and say that it is expensive.
But my position is this: never spare money on food and then you won’t need to spend money on expensive medicines.
Saving on your health is short-sighted and unwise; health is not a gift from nature, it is the result of our care.
Vegetable oil is a product obtained from seeds, fruits, roots and other parts of various gifts of nature, and is the most common available fat in the human diet. Vegetable oils were also used for culinary purposes, this can be confirmed by absolutely any national culinary school. This product was the most common means of preserving beauty; cosmetics based on vegetable oils both in ancient centuries and in our time occupy a leading position among all those presented. And of course, one of the most popular roles of vegetable fats was that of a health savior. And now this product will always be one of the first to be purchased by supermarket visitors. Fans of traditional medicine and admirers of home cosmetology also cannot do without this gift of nature.
Useful properties of the product
The beneficial properties of vegetable oils are that they are a product consisting of waxes, phosphatides and triglycerides. Their composition is additionally enriched with such components as free fatty acids, lipochromes, tocopherols, vitamins and many additional beneficial substances. All these components are essential for the human body to function properly. Scientists have proven that a lack of vegetable oils in the daily diet can lead to various bad consequences, including the development of diseases, such as impaired cholesterol metabolism and the occurrence of atherosclerosis, and its regular use, on the contrary, reduces the chance of developing these diseases to a minimum, additionally supplying the body with the necessary set of nutrients.
The composition and chemical set of vegetable oils very much depends on what kind of processing it went through and from what product it was obtained. But what all vegetable oils have in common is that they are rich in alphalinolic acid (omega 3), which:
- It is necessary for people suffering from diabetes to maintain normal body and blood sugar levels.
- In the presence of cardiovascular diseases, it strengthens the walls of blood vessels.
- In the case when vision problems are diagnosed, it serves as an additional component that helps restore the required level.
- Strengthens the immune system, helping the body cope with pathogens.
- Helps with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
The second important component in the composition of vegetable oils is linoleic acid (omega 6), the only acid that can be reformed into other acids, thus compensating for their deficiency. The lack of this acid is especially dangerous for young children, because it leads to:
- Slow development of a small organism.
- Diseases of the epidermis.
- Digestive disorders.
Vegetable oils contain a large amount of tocopherol (vitamin E). This determines the following positive qualities of this product:

In addition to the above, vegetable oils are rich in phytosterols, phosphatides, pigments and many other substances that give color to this product, ensure its long-term storage, aroma and taste. And at the same time, they also have a beneficial effect on the health of the liver, strengthen its cells, helping it perform its cleansing function. They also normalize metabolism in the body and help produce bile. An insufficient amount of these components of vegetable oils can cause the development of atherosclerosis and anemia.
Vegetable oil production
Vegetable oil production now exists in every corner of the globe. In each region, it is obtained from plants characteristic of that particular region. Get them from:

- Oilseeds, for example, from mustard, sunflower, soybean, poppy, rapeseed, flax, cotton, etc.
- Fruits of oilseed plants.
- When processing plant raw materials– tomatoes, rice, wheat germ, almonds, corn, apricots, etc.
- Orekhov, Almost all nuts are suitable for producing oil.
The process of extracting oil from the base can be done in two ways, which are radically different from each other:
- Pressing- consists of a mechanical effect on plant raw materials, in other words, they squeeze it out. It was in this way that vegetable oil was obtained in ancient times. And now nothing has changed. The oil obtained in this way has the maximum amount of useful substances, it retains its natural structure. Pressing can be carried out using both hot and cold methods. When hot, the vegetable base is first fried. This allows you to increase the amount of product obtained, which will also have a richer taste and aroma. But this method shortens the shelf life. The cold method does not involve thermal processing of raw materials, so the oil obtained this way can be stored longer.
- Extraction– this type of production of a certain vegetable oil is based on its ability to dissolve in special organic solvents. A solvent is repeatedly passed through the raw material, completely removing the oil from the plant base. After this, the solvent is distilled off, and we get pure oil. This method allows you to increase the amount of product obtained.
What types of vegetable oil are there?
Types of vegetable oil are now presented in a wide range. Due to the fact that oil is obtained from plant products, there are a huge number of types of this product. Each country has its own preferences, primarily related to the flora growing there. But, nevertheless, we can distinguish the main types that are most widespread on the world market:

- sunflower;
- olive;
- rapeseed;
- peanut;
- sesame.
- from grape seeds;
- mustard;
- corn;
- soy;
- linen;
- cotton
In addition to these, there are also a huge number of other types, such as pumpkin, walnut and many others. It is impossible to single out the best vegetable oil from this series, because each has its own remarkable characteristics and areas of use.
 Most often we buy refined oil for food consumption; it is this oil that is mainly presented on store shelves. What does this word mean?
Most often we buy refined oil for food consumption; it is this oil that is mainly presented on store shelves. What does this word mean?
The refining process involves various types of purification of oil obtained by cold or hot pressing. This product is most often refined in order to clean it from impurities and various substances that shorten its shelf life. In addition, refining allows you to get rid of the specific taste of the plants from which the oil was pressed. This is very important for culinary purposes, because when preparing various dishes, the natural taste, for example, of sunflower oil, can spoil the result and interrupt the taste of the prepared products.
But the negative side of refining can be considered the almost complete cleansing of vitamins and other useful substances in the oil.
Use in cooking
 On store shelves we can see a huge variety of products in this category. You shouldn’t limit yourself in the kitchen to just one, for example, sunflower oil. By diversifying your supplies with various aromatic bottles, you can significantly expand your daily diet, enriching it with new flavors. In addition, in this way you enrich the prepared dishes with very useful vitamins and microelements, which are so necessary in our time, characterized by fast pace, lack of healthy food and snacks on the go.
On store shelves we can see a huge variety of products in this category. You shouldn’t limit yourself in the kitchen to just one, for example, sunflower oil. By diversifying your supplies with various aromatic bottles, you can significantly expand your daily diet, enriching it with new flavors. In addition, in this way you enrich the prepared dishes with very useful vitamins and microelements, which are so necessary in our time, characterized by fast pace, lack of healthy food and snacks on the go.
Some varieties and types should be used for frying foods, others can be very useful for seasoning salads or preparing marinades, while others will add more flavor to your desserts and confectionery products.
 Unrefined sunflower oil will add incredible flavor to any salad. Olive oil can generally be considered a storehouse of vitamins and a hallmark of Mediterranean cuisine, so pizza and pasta are impossible without this elixir of youth.
Unrefined sunflower oil will add incredible flavor to any salad. Olive oil can generally be considered a storehouse of vitamins and a hallmark of Mediterranean cuisine, so pizza and pasta are impossible without this elixir of youth.
Dough made with vegetable oil will help you, while fasting, continue to delight your family members with delicious pastries and aromatic baked goods.
Cabbage with vegetable oil, an ordinary light salad, will save you in case of unexpected guests. And creamy vegetable oil, which has now appeared on store shelves, will allow you to enjoy your usual sandwiches for breakfast, reducing the harm of this animal product.
Mix salt and vegetable oil, whatever you like, and you will get a wonderful marinade for meat, poultry or fish.
By alternating rapeseed, soybean, sesame, peanut and pumpkin oil in the preparation of familiar dishes, you will allow your usual food combinations to sparkle with new notes, which means your culinary masterpieces will never be repeated.

Despite the rather high calorie content of vegetable oil, approximately 1000 kcal per 100 g. product, you should not be afraid of the possibility of gaining excess weight. Still, as a rule, a very small dose of this product is used for one meal. In addition, the fats included in this product are very easily absorbed by the body.
Vegetable table oils spoil very easily, so you must strictly follow their storage conditions: keep in a glass container with a tightly screwed lid or stopper, protect from sunlight and strictly adhere to the expiration date. In this case, they will bring nothing but benefit!
Application in cosmetology
Vegetable oil has been used in cosmetology for a very long time. Even ancient beauties noticed that various types of this useful gift of nature are able to cope with many cosmetological problems and give beauty to the skin, hair and nails. Oils obtained from seeds, seeds of various plants and nuts are still used in the production of various personal care products.
The composition of this product is perfectly balanced and similar to the composition of sebum, which allows it to be easily absorbed by our skin. Well, the variety of types of oils and the functions they perform will allow every beauty to choose the ideal product for herself. After gaining some experience, you can easily even create a mixture of vegetable oils, taking into account the characteristics of your skin type.
For example, for dry aging skin The best care products will be avocado, rosehip, and wheat germ oils. Olive, sea buckthorn and peach oils are ideal. Sensitive skin will easily accept castor or peach oil, without irritation or allergies. A oily, combination type“with delight” to get acquainted with grape seed, hazelnut, jojoba, and olive oils.
 Even our great-grandmothers trusted castor and burdock oils for hair care, thanks to which they could be proud of their braids into old age. You can use this recipe: heat 1 tbsp. castor or burdock oil and rub into the hair roots. Then wrap your head in a warm towel and hold for an hour. If you use this recipe twice a week, after a couple of months you will notice that your curls have become thicker and have a healthy shine. And hair growth and the appearance of new ones will not keep you waiting.
Even our great-grandmothers trusted castor and burdock oils for hair care, thanks to which they could be proud of their braids into old age. You can use this recipe: heat 1 tbsp. castor or burdock oil and rub into the hair roots. Then wrap your head in a warm towel and hold for an hour. If you use this recipe twice a week, after a couple of months you will notice that your curls have become thicker and have a healthy shine. And hair growth and the appearance of new ones will not keep you waiting.
Nails, for example, will become stronger and grow faster if you use almond or apricot oil for warm baths.
The benefits of vegetable oil and treatment
The benefits of vegetable oil have long been familiar to people, which is why both traditional and folk medicine successfully use vegetable oils to treat various diseases.
 For example, in industry, in the manufacture of medicines, such a component is successfully used for external use in order to create a greenhouse effect, due to which medicinal substances penetrate deeper into the skin. And the oils themselves have a fairly wide range of useful functions.
For example, in industry, in the manufacture of medicines, such a component is successfully used for external use in order to create a greenhouse effect, due to which medicinal substances penetrate deeper into the skin. And the oils themselves have a fairly wide range of useful functions.
Traditional medicine is literally saturated with various beneficial vegetable oils, which are used both for external and internal use. Let us give an example of several types of oils with recipes for their use.
Linseed oil:
- To prevent cardiovascular diseases, you need to consume one teaspoon of flaxseed oil every day.
- For a sore throat, gargle with warm flaxseed oil. Take one tablespoon of warm product into your mouth and roll from cheek to cheek for five minutes. Then spit it out.
- In case of frostbite, apply a compress with this oil to the damaged part of the skin for 20 minutes.
Sesame oil:
- Toothache can be easily dealt with by rubbing sesame oil into the inflamed gum.
- For otitis media, place warm oil in the ear.
- To normalize digestion during constipation, drink one tablespoon of the product every day on an empty stomach.
Sunflower oil:
- To treat rheumatism, heat one glass of sunflower vegetable oil and add 4 hot red peppers. Infuse the medicine for two weeks, and then rub the sore area.
- For sinusitis, suck one tablespoon of the product every day like a lollipop.
Olive oil:
- For regular headaches, drink two teaspoons of olive oil every morning and evening before meals.
- Chapped lips will “come to life” thanks to a compress of this oil.
- To combat cough, drink one teaspoon of warm oil twice a day.
The scope of application of this product in medicine is unusually wide. And this is not surprising; it is difficult to find such a unique combination of a variety of product types with an incredible number of beneficial properties and medicinal functions.
Harm of vegetable oil and contraindications
The harm of vegetable oil and contraindications to its use are so small that you just need to know some rules for choosing the necessary product and the specifics of its use in order to reduce the negative impact to zero:

In this article we will talk about the unique properties of base oils. competes with the most expensive and elite creams, second only to them in price :) . In addition, 100% natural oils do not contain preservatives, fragrances or other toxic components.
Vegetable oils are divided into base and essential.
Base oils according to biochemical parameters similar to skin properties, which allows them to penetrate into the deep layers of the epidermis and deliver healing substances there. Therefore, they are also called carrier oils, transport or carrier oils.
They can be used as an independent cosmetic product, and as a basis for mixing with essential oils and other ingredients.
When buying base oils, pay attention to the composition, it should not contain synthetic impurities, dyes, or preservatives.
To produce 100% pure vegetable oils, the cold pressing method is used and subsequent high-quality filtration without the use of high temperatures. This method preserves all the valuable properties of the oil and extends its shelf life.
Base oils have unique regenerating, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant properties, which is due to their composition: saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, macro- and microelements, vitamins, phytosterols, phospholipids.
Well absorbed by the body, oils participate in chemical processes and are a natural stimulator of the most important biochemical and physiological processes:
- accelerate cellular metabolism;
- improve skin nutrition;
- promote the synthesis of fibrinogen and collagen;
- improve lymph and blood circulation;
- increase skin tone;
- effectively cleanse the skin while nourishing it;
- normalize the secretion of the sebaceous glands.
Fatty acid
The unique healing properties of many oils are due to the presence of fatty acids in their composition, which are divided into saturated and unsaturated.
With a high content of saturated acids, oils will be solid even at room temperatures. The lower the acid content, the softer the oil.
Unsaturated fatty acids have great value for the body: they actively participate in metabolic processes, in the synthesis of prostaglandins, which regulate the production of hormones necessary for the body. The higher the content of unsaturated acids in the oil, the more liquid it is.
Oleic monounsaturated fatty acid, which is responsible for the construction of biological membranes in the human body, has especially valuable properties. Oils containing it in large quantities are easily absorbed and absorbed by the skin. Olive oil is the richest in oleic acid (up to 85%).
Many unsaturated acids are not synthesized by our body and can only be obtained through food or through the skin. They are called essential fatty acids (omega 6 and omega 3), they are vital for the health of the skin and the body as a whole. These include linoleic, linolenic, gamma-linolenic acids, as well as their derivatives.
Deficiency of essential acids leads to:
- to damage the skin barrier, as a result of which microorganisms, allergens, harmful substances easily penetrate into it, inflammatory reactions and skin diseases occur;
- to transepidermal loss of moisture;
- to chronic degenerative diseases such as cancer, heart disease, hypertension and diabetes;
- to deterioration of brain function.
Signs of essential acid deficiency: peeling of the skin, feeling of dryness, increased irritability and sensitivity of the skin, itching, redness.
To permanently eliminate these unpleasant symptoms It is necessary to introduce natural fats and oils containing essential fatty acids into the diet and skin care.
Best sources of essential fatty acids oils of borage (borage), black currant, and aspen (evening primrose) are considered. Gamma linolenic acid contained in these oils
- stops
- normalizes hormone levels, reduces skin oiliness,
- suppresses the formation of melanin, brightens the skin.
Useful to use internally:
- flaxseed oil (the required daily balance of essential fatty acids is contained in one or two tablespoons). Before using oil, be sure to read the contraindications!
- Fish oil (salmon, mackerel, salmon, sardines, eel, etc.),
- pumpkin seeds, flaxseeds, soybeans, wheat germ, nuts.
So, let's summarize and list
oils to look for if you are deficient in essential fatty acids
Liquid oils:
In the following publications:
- what oils are suitable for .
Come in for beauty recipes!
Each capsule (0.2 g) contains 0.084 mg of carotenoids from sea buckthorn oil concentrate, the recommended daily dose of the product provides 6-12% of the physiological requirement for beta-carotene.
In addition to carotenes, sea buckthorn oil also contains a number of biologically active compounds: vitamins B1, B2, C, P, K, E; flavonoids - isorhamnetin, quercetin, kaempferol, myricetin, catechin, which have capillary-strengthening, cardio-stimulating, gastroprotective, diuretic, anti-inflammatory effects; chlorogenic acid, which has a choleretic effect; beta-sitosterin, choline, which stimulates the synthesis of phospholipids, has a lipotropic effect, prevents fatty liver, enhances phagocytosis, helps improve memory, especially in old age, and has a sedative effect; alpha and beta amirins are compounds that regulate lipid metabolism.
- healthy people for the prevention of A-hypovitaminosis, to increase the body's defenses, to improve the condition of skin, nails and hair, for children to ensure normal growth, for elderly people for active longevity, to maintain the antioxidant defense system, especially for people living in environmentally unfavorable areas, as well as those exposed to various types of household radiation (working with a computer, prolonged exposure to the sun);
- as a therapeutic food product for eye diseases, decreased vision, skin diseases, accompanied by dryness and slow regeneration, for chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract(inflammatory and ulcerative-erosive lesions), bronchi, lungs, tuberculosis, In this case, the main treatment of diseases should be entrusted to a doctor.
- healthy people for the prevention of E-hypovitaminosis, to maintain systems antioxidant protection of the body, especially for residents of industrial areas, centers of large cities, computer users, people exposed to the sun for a long time; children for normal growth, elderly people to slow down the aging process, to improve the condition of skin, nails and hair;
- for the prevention of disorders of linide metabolism and atherosclerosis;
- as a therapeutic food product for muscular dystrophies, degenerative changes in bones, joints, ligaments, including post-traumatic ones, with reduced function of the gonads, with menopause, with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, with diseases of the heart and peripheral vessels, while the main treatment of the above diseases should be entrusted to a doctor.
- for healthy people as a source of unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, essential amino acids, vitamins, microelements that have a general strengthening effect on the body;
- for the prevention of lipid, protein, water-salt metabolism disorders;
- as a therapeutic food product for diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract(chronic glomerulo- and pyelonephritis, cystitis, urolithiasis), for osteoporosis. The main treatment of these diseases should be entrusted to a doctor.
Vegetable oils
Consists of a mixture of sunflower, mustard, linseed and sesame oils.
The combination of four vegetable oils differing in composition (Table 1) optimizes the ratio of fatty acids of various classes (Table 1), enriches the amino acid, vitamin and mineral composition of the mixture.
This functional food product that with regular use supplies the body with essential nutritional factors and promotes good physical development. Flaxseed oil regulates the processes of growth and development of the brain, eyes, gonads, gastrointestinal tract, musculoskeletal system, and enhances tissue regeneration. Sesame oil is a valuable dietary food product that has a beneficial effect on health. In medicine, it is used for therapeutic nutrition for lipid metabolism disorders, arterial hypertension, and inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the joints. In recent years, sesame seeds and sesame oil have been actively used for the prevention of osteoporosis, due to the presence of calcium, phosphorus - building materials for bone tissue, and phytoestrogens, which control the processes of bone resorption. In bodybuilding sesame oil is consumed to increase muscle mass. Sunflower oil is an additional source of essential amino acids and magnesium. Mustard oil improves appetite, stimulates digestion processes, promotes better absorption of nutrients. It should be noted that for good physical development, not only good nutrition is important, but also high physical activity.
Consists of a mixture of corn, mustard and pumpkin oils.
This mixture combines three oils that have an effect on the organs of the digestive system. Corn oil enhances the secretion of bile, reduces its viscosity, and has an antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory effect. Mustard oil improves appetite, stimulates digestion, and has bactericidal and anthelmintic activity. Pumpkin oil enhances the motor function of the colon and bile ducts and has an anthelmintic effect.
Consists of a mixture of corn, mustard, camelina oils and rosehip oil.
It has an original aroma and taste, it combines the fresh pungent aroma and taste of camelina and mustard oils, and the softness of corn oil. The high taste of this oil is not inferior to its beneficial properties. Corn and mustard oils are rich in linoleic (omega-6) oleic acid but low in alpha-linolenic (omega-3) acid; camelina oil is the “champion” in terms of alpha-linolenic acid content, and contains linoleic and oleic acids in smaller quantities (Table 1); rosehip oil is a rich source of gamma-linolenic acid. The combination of these oils makes the ratio of fatty acids more harmonious, capable of regulating the content of lipids and cholesterol in the blood. Tocopherols, carotenoids, phospholipids, bioflavonoids contained in all components of the mixture form an antioxidant complex. The anti-atherosclerotic, anti-inflammatory, regenerating, tonic, antispasmodic, choleretic, bactericidal, anthelmintic effect of the components of the oil mixture determines its positive effect on almost all systems of the human body.
LITERATURE
1. Bakhtin Yu.V. The effectiveness of using cedar oil in the complex treatment of patients with arterial hypertension / Bakhtin Yu.V., Budaeva V.V., Vereshchagin A.L. and others // Nutrition issues. 2006. T. 75, No. 1. p. 51 - 53.
2. Biologically active substances of plant origin. In three volumes. T. I / B.N. Golovkin, Z.N. Rudenskaya, I.A. Trofimova, A.I. Schröter. - M: Nauka, 2001. 350 p.
3. Biologically active substances of plant origin. In three volumes. T. II / B.N. Golovkin, Z.N. Rudenskaya, I.A. Trofimova; A.I. Schröter. - M.: Nauka, 2001. 764 p.
4. Biologically active substances of plant origin. In three volumes. T. III / B.N. Golovkin, Z.N. Rudenskaya, I.A. Trofimova, A.I. Schröter. - M.: Nauka, 2001. 216 p.
5. Gorbachev V.V., Gorbacheva V.N. Vitamins, macro- and microelements. Directory. -Minsk: Book House; Interpressservice, 2002. 544 p.
6. Makarenko SP. Fatty acid composition of endosperm and seed germ lipids Pinus sibirica And Pinus sylvestris / Makarenko SP., Konenkina T., Putilina T.E. and others // Plant Physiology. 2008. T.55, No. 4. With. 535 - 540.
7. Nechaev A.P. Key trends in the production of oil and fat products / Nechaev A.P. //Products & profit. 2011. No. 2. p. 6 - 9.
8. Skakovsky E.D. NMR analysis of pine nut oils (Pinus sibirica) and seeds of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) I Skakovsky E.D., Tychinskaya L.Yu., Gaidukevich O.A. and others // Journal of Applied Spectroscopy. 2007. T.74, No. 4. p. 528 - 532.
9. Smolyansky B.L., Liflyandsky V.G. Dietetics. The latest reference book for doctors. St. Petersburg: Sova; M.: Eksmo Publishing House, 2003. 816 p.
10. Tables of the chemical composition and calorie content of Russian food products / Skurikhin I.M. Tutelyan V.A. . - M.: DeLi print, 2007. 276 p.
11. Ariel A. Resolvins and protectins in the termination program of acute inflammation / Ariel A., Serhan C.N. // Trends Immunol. 2007. Vol. 28, No. 4, P. 176-183.
12. Brochot A. Effects of alpha-linolenic acid vs. docosahexaenoic acid supply on the distribution of fatty acids among the rat cardiac subcellular membranes after a short- or long-term dietary exposure / Brochot A., Guinot M., Auchere D. // Nutr Metab (Lond). 2009; 6:14. Published online 2009 March 25. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-6-14.
13. Calder PC Polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: New twists in an old tale / Calder PC // Biochimie. 2009. Vol.91, No. 6. P. 791-795.
14. Campos H. Linolenic Acid and Risk of Nonfatal Acute Myocardial Infarction / Campos H., Baylin A., Willett W.C. //Circulation. 2008. Vol.118. P. 339-345.
15. Chang CS. Gamma-linolenic acid inhibits inflammatory responses by regulating NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages / Chang C.S., Sun H.L., Lii C.K. //Inflammation. 2010. Vol. 33, No. 1. P. 46-57.
16. Chapkin R.S. Bioactive dietary long chain fatty acids: Emerging mechanisms of action / Chapkin R.S. McMurray D.N., Davidson L.A. // Br J Nutr. 2008. Vol. 100, No. 6. P. 1152-1157.
17. Chilton F.H. Mechanisms by which botanical lipids affect inflammatory disorders / Chilton F.H., Rudel L.L., Parks J.S. //American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Vol. 87, No. 2, 498S-503S.
18. Das U. N. Essential fatty acids and their metabolites could function as endogenous HMG-CoAreductase and ACE enzyme inhibitors, anti-arrhythmic, anti-hypertensive, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective, and cardioprotective molecules / Das U. N. // Lipids Health Dis. 2008; 7: 37. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-7-37.
19. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic disease. Report of the Joint WHO/FAO Expert consultation. Geneva.: WHO, 2002.
20. Djousse L. Dietary Linolenic Acid Is Inversely Associated With Calcined Atherosclerotic Plaque in the Coronary Arteries / Djousse L., Arnett D.K., Carr J.J. et al. // Circulation. 2005. Vol. 111. P. 2921-2926.
21. Egert S. Dietary a-Linolenic Acid, EPA, and DHA Have Differential Effects on LDL Fatty Acid Composition but Similar Effects on Serum Lipid Profiles in Normolipidernic Humans / Egert S., Kannenberg F., Somoza V. et al. // J. Nutr. 2009. Vol.139, No. 5. P. 861 - 868.
22. Fetterman J. W. Therapeutic potential of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in disease / Fetterman J. W., Zdanowicz M. M. //Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2009. Vol.66, No. 13. P. 1169-1179.
23. Harris W. S., Alpha-Linolenic Acid. A Gift From the Land? //Circulation. 2005. Vol. 111. P. 2872 - 2874.
24. Hughes G.M. The effect of Korean .pine nut oil (PinnoThin™) on food intake, feeding behavior and appetite: A double-blind placebo-controlled trial /Hughes G.M., Boyland E.J., Williams N.J. et.al. // Lipids Health Dis. 2008; 7: 6. Published online 2008 February 28. doi: 10.1186/1476-51 3X-7-6.
25. Jequier E. Leptin signaling, adiposity, and energy balance // Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. Vol. 967, No. 6. P. 379-88.
26. Jicha G. A. Omega-3 fatty acids: potential role in the management of early Alzheimer's disease / Jicha G. A., Markesbery W. R. // Clin Interv Aging. 2010. Vol. 5. P. 45-61.
27. Kapoor R. Gamma linolenic acid: an antiflammatory omega-6 fatty acid / Kapoor R., Huang Y.S. // Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2006. Vol.7, No. 6. P. 531-534.
28. Kris-Etherton P.M. The Role of Tree Nuts and Peanuts in the Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease: Multiple Potential Mechanisms /Kris-Etherton P.M., Hu F.B. // J. Nutr. 2008. Vol. 138, No. 9. P. 1746S-1751S.
29. Lauretani F. Omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids predict accelerated decline of peripheral nerve function in older persons /Lauretani F, Bandmelli F., Benedetta B. // J Neurol. 2007. Vol. 14, No. 7. P. 801-808.
30. Lin Y.H.Whole body distribution of deuterated linoleic and alpha-linolenic acids and their metabolites in the rat / Lin Y.H., Salem N. Jr.// J Lipid Res. 2007. Vol.48, No. 12. P.2709-2724.
31. Molendi-Coste O. Why and How Meet n-3 PUFA Dietary Recommendations?/ Molendi-Coste O., LegryV, Leclercq LA. // Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2011; 2011: 364040. Published online 2010 December 8. doi: 10.1155/2011/364040.
32. Myhrstad M. C. W. Effect of marine n-3 fatty acids on circulating inflammatory markers in healthy subjects and subjects with cardiovascular risk factors /Myhrstad M. C. W., Retterstol K., Telle-Hansen V. H.// InflammRes. 2011. Vol. 60, No. 4. P. 309-319.
33. Newell 1-McGloughlin M. Nutritionally Improved Agricultural Crops / Newell-McGloughlin M. // Plant Physiol. 2008. Vol. 147, No. 3. P. 939-953.
34. Pasman W.J. The effect of Korean pine nut oil on in vitro CCK release, on appetite sensations and on gut hormones in post-menopausal overweight women / Pasman W.J., Heimerikx J., Rubingh CM. // Lipids Health Dis. 2008; 7: 10. Published online 2008 March 20. doi:10.1186/1476-511X-7-10.
35. Rodriguez-Leyva D. The cardiac and haemostatic effects of dietary hempseed / Rodriguez-Leyva D., Grant N Pierce G.N. // Nutr Metab (Lond). 2010; 7: 32. Published online 2010 April 21. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-7-32.
36. Schwartz J. PUFA and LC-PUFA intake during the first year of life: can dietary practice achieve a guideline diet? /Schwartz J., Dube K., Alexy U. /7 Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010. Vol. 64, No. 2. P. 124-130.
37. Song L-Y. Identification and functional analysis of the genes encoding A6-desaturase from Ribes nigrumf/ Song Li-Ying, Wan-Xiang Lu, Jun Hu // J Exp Bot. 2010. Vol. 61, No. 6. P. 1827-1838.
38. Weaver K. L. Effect of Dietary Fatty Acids on Inflammatory Gene Expression in Healthy Humans / Weaver K. L. Ivester P., Seeds M. // J Biol Chem. 2009. Vol. 284, No. 23. P. 15400-15407.
39. Winnik S. Dietary a-linolenic acid diminishes experimental atherogenesis and restricts T cell-driven inflammation / Winnik S., Lohmann C, Richter E.R. et al. // Eur Heart J (2011) doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq501.
40. Wolff R.L. Fatty acid composition of Pinaceae as taxonomic markers /Wolff R.L., Lavialle O., Pedrono F. et al. // Lipids. 2001. Vol. 36, No. 5. P. 439-451.
41. Wolff R.L. General characteristics of Pinus spp. seed fatty acid compositions, and importance of delta5-olefinic acids in the taxonomy and phylogeny of the genus / Wolff R.L., Pedrono F., Pasquier E. // Lipids. 2000. Vol. 35,-No. 1. P.l -22.
42. Wolff RL Fatty acid composition of some pine seed oils / Wolff RL, Bayard CC. // JAOCS. 1995. Vol.72. P. 1043-1045.
43. Zarevucka M. Plant Products for Pharmacology: Application of Enzymes in Their Transformations / Zarevucka M.. Wimmer Z. // Int J Mol Sci. 2008. Vol. 9, No. 12. P. 2447-2473.
1 when 1 g of fat is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, 9 kcal is formed, when 1 g of proteins or carbohydrates is oxidized - approximately 4 kcal,
2, under the influence of desaturases, desaturation occurs, double bonds are formed, from lat. saturatio - saturation,
3 elongases lengthen the carbon chain, from lat. elongatio - stretching, lengthening.