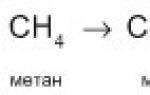
Preparations containing choline. Vitamin B4 (Choline)
Vitamins combined into group B are very important for maintaining the health of children and the active development of the child’s body. Among them, one of the most valuable for the nervous system is called vitamin B4, another name for which is “choline”. How is this vitamin substance useful for children, what food can it be obtained from, and can choline be given in the form of vitamin supplements?
 For the active growth and development of a child’s body, a sufficient supply of vitamin B4 is important.
For the active growth and development of a child’s body, a sufficient supply of vitamin B4 is important.
Benefits of Choline
The main functions of vitamin B4 are participation in fat metabolism and support of cell membranes. This substance is important for liver function and was first isolated from bile, hence its name “choline”.
An equally valuable effect of vitamin B4 is supporting the functioning of the nervous system. Thanks to its participation in the production of acetylcholine, this vitamin promotes the rapid conduction of nerve impulses. A sufficient amount of choline has a positive effect on mental processes such as memory and attention.
In addition, choline:
- Improves the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
- Lowers blood cholesterol levels.
- Prevents excess bile formation and gallstones.
- Accelerates the recovery of liver cells after toxic damage.
- Increases resistance to stress and improves mood, preventing depression.
- Normalizes metabolic processes, helping to maintain body weight.
- Strengthens the heart muscle and blood vessel walls.
- Participates in the synthesis of insulin and hormonal compounds.
- Supports the work of lecithin and the effect of other B vitamins.
An increased need for choline is noted during significant physical activity and frequent stressful situations.
 Exercising increases your baby's need for choline
Exercising increases your baby's need for choline
Choline Products
Every day a child should receive approximately 100-350 milligrams of choline, and the main source of this substance is food.
Vitamin B4 is found in significant amounts in:
- Eggs.
- Liver.
- Meat.
- Sour cream and cream.
- Bran.
- Sunflower oil.
- Nuts.
- Green tea.
- Trout, herring and mackerel.
- Yeast.
- Sunflower seeds.
- Cabbage, carrots, spinach and tomatoes.
- Green peas.
- Fermented milk products.

Review of drugs
If a mother wants to supplement the children’s diet with vitamin B4 from pharmacy supplements, then the child can receive choline from the following multivitamin complexes:
- Univit Kids with Omega-3 and choline. The supplement is prescribed for children over 3 years of age and consists of chewable cherry dolphin gummies. From one tablet the child will receive 35 mg of choline. The product also contains ascorbic acid, other B vitamins and Omega-3 fats.

- Supradin Kids. These marmalade “fish” and “stars” are given to children over 3 years old. From one lozenge of this complex the child will receive 30 mg of vitamin B4. The preparation also contains other vitamins and omega-3 fats that are important for children.

- Supradin Kids Junior. The complex is designed for children over 5 years old and contains essential vitamins and valuable minerals. It is produced in the form of chewable tablets with a tangerine-orange flavor. One tablet of this supplement contains 25 mg of choline.

- VitaMishki Bio+. This supplement is allowed from the age of three. It is represented by chewable “bear cubs”, which contain not only vitamins, but also prebiotics. The choline content in one lozenge of this drug is 20 mg.

- Solgar Kangavites Multivitamins and Minerals. The supplement is prescribed to children over 2 years of age and is presented as fruit or berry chewable tablets. They include important vitamin compounds, mineral salts, citrus bioflavonoids, rose hips and other natural ingredients. Choline in one tablet of this drug contains 0.5 mg.
Hello friends. Today I am going to tell you about a special element. This water-soluble nutrient is choline. It is also called vitamin B4. But in fact, it is neither a vitamin nor a mineral. Today we’ll talk about what hides behind this vitamin-like substance and where it is found :)
By the way, this element was discovered back in the 19th century. It was discovered during a study of animal bile. That is why it received the name “choline” (from the Greek choly - “bile”). And the importance of B4 for the human body was realized only in the 30s of the last century.
It is a microelement that performs the following functions:
- supports the health of the reproductive system;
- reduces homocysteine and protects the heart;
- improves the functioning of the digestive tract;
- normalizes insulin levels;
- prevents premature aging of the body;
- protects against the development of Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia.
This vitamin-like substance is essential for liver function and normal brain and nervous system development. B4 is also important for muscle movement, it supports healthy metabolism and increases energy.

In food it is often present in the form of phosphatidylcholine. This compound can be found in a variety of foods that contain certain fats.
Deficiency Symptoms
Most people do not get enough B4, despite the presence of sources in their diet. This happens because some types of choline are hardly absorbed by the body. Research shows that the average person does not have the level of B4 they need on a daily basis ( 1 ).
Most likely, this is due to genetic factors - when people have an increased need for choline. Researchers are still debating how much B4 you should consume daily. So far they have not come to an agreement, since the needs are too individual. Therefore, the recommendations for use given in the table below are rather arbitrary.
Symptoms of element B4 deficiency:
- fatigue, low energy level;
- memory loss, decreased cognitive abilities;
- muscle pain;
- nerve damage;
- mood swings, frequent disorders;
- sleep disorders.

With age, with B4 deficiency, cognitive abilities decrease. This is manifested by memory loss, Alzheimer's disease and dementia. Adequate levels of choline support neurotransmitters ( 2 ).
Where is vitamin B4 found?
Our body can produce a small amount of choline on its own, but we must get the rest from food. Therefore, following a diet is the best way to provide the body with the necessary amount of B4. A large percentage of this substance is found in animal products. Therefore, vegetarians and vegans are more susceptible to deficiency.
B4 can be obtained from natural foods, including eggs, liver, beef, salmon, cauliflower or Brussels sprouts. Eggs are sometimes called "brain food" because they contain high amounts of choline.
And here are the leading products in terms of the content of this vitamin-like element. Data are based on a daily intake of 500 mg.
| B4 content, mg per 100 g. product | Percentage of daily value, % | |
| Beef liver | 635 | 127 % |
| Egg | 251 | 50,2 % |
| Chicken liver | 200 | 40 % |
| Lentils | 200 | 40 % |
| Lamb, 1 cat | 90 | 18 % |
| Oat groats | 90 | 18 % |
| Beef, tenderloin | 70 | 14 % |
| Turkey breast | 66,4 | 13,3 % |
| Peas, grain | 50 | 10 % |
| Spinach | 20 | 3,9 % |
Like many vitamins, choline loses some during heat treatment. For example, when cooking meat, approximately 20% of choline “evaporates”, and up to 40% of plant foods. Approximately 3%-5% is lost during baking. But this does not mean that you should eat meat raw :) Just do not boil or fry the food too much.

Instructions for use
Choline is still being studied. Scientists are eager to learn more about its potential benefits to the body. The amount of B4 listed below is sufficient to obtain optimal benefits without causing any harm to the body. According to methodological recommendations MP 2.3.1.2432-08 dated December 18, 2008, the following consumption standards have been established in Russia:
For children
Hello friends. Today I am going to tell you about a special element. This water-soluble nutrient is choline. It is also called vitamin B4. But in fact, it is neither a vitamin nor a mineral. Today we’ll talk about what hides behind this vitamin-like substance and where it is found :)
By the way, this element was discovered back in the 19th century. It was discovered during a study of animal bile. That is why it received the name “choline” (from the Greek choly - “bile”). And the importance of B4 for the human body was realized only in the 30s of the last century.
It is a microelement that performs the following functions:
- supports the health of the reproductive system;
- reduces homocysteine and protects the heart;
- improves the functioning of the digestive tract;
- normalizes insulin levels;
- prevents premature aging of the body;
- protects against the development of Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia.
This vitamin-like substance is essential for liver function and normal brain and nervous system development. B4 is also important for muscle movement, it supports healthy metabolism and increases energy.

In food it is often present in the form of phosphatidylcholine. This compound can be found in a variety of foods that contain certain fats.
Deficiency Symptoms
Most people do not get enough B4, despite the presence of sources in their diet. This happens because some types of choline are hardly absorbed by the body. Research shows that the average person does not have the level of B4 they need on a daily basis ( 1 ).
Most likely, this is due to genetic factors - when people have an increased need for choline. Researchers are still debating how much B4 you should consume daily. So far they have not come to an agreement, since the needs are too individual. Therefore, the recommendations for use given in the table below are rather arbitrary.
Symptoms of element B4 deficiency:
- fatigue, low energy level;
- memory loss, decreased cognitive abilities;
- muscle pain;
- nerve damage;
- mood swings, frequent disorders;
- sleep disorders.

With age, with B4 deficiency, cognitive abilities decrease. This is manifested by memory loss, Alzheimer's disease and dementia. Adequate levels of choline support neurotransmitters ( 2 ).
Where is vitamin B4 found?
Our body can produce a small amount of choline on its own, but we must get the rest from food. Therefore, following a diet is the best way to provide the body with the necessary amount of B4. A large percentage of this substance is found in animal products. Therefore, vegetarians and vegans are more susceptible to deficiency.
B4 can be obtained from natural foods, including eggs, liver, beef, salmon, cauliflower or Brussels sprouts. Eggs are sometimes called "brain food" because they contain high amounts of choline.
And here are the leading products in terms of the content of this vitamin-like element. Data are based on a daily intake of 500 mg.
| B4 content, mg per 100 g. product | Percentage of daily value, % | |
| Beef liver | 635 | 127 % |
| Egg | 251 | 50,2 % |
| Chicken liver | 200 | 40 % |
| Lentils | 200 | 40 % |
| Lamb, 1 cat | 90 | 18 % |
| Oat groats | 90 | 18 % |
| Beef, tenderloin | 70 | 14 % |
| Turkey breast | 66,4 | 13,3 % |
| Peas, grain | 50 | 10 % |
| Spinach | 20 | 3,9 % |
Like many vitamins, choline loses some during heat treatment. For example, when cooking meat, approximately 20% of choline “evaporates”, and up to 40% of plant foods. Approximately 3%-5% is lost during baking. But this does not mean that you should eat meat raw :) Just do not boil or fry the food too much.

Instructions for use
Choline is still being studied. Scientists are eager to learn more about its potential benefits to the body. The amount of B4 listed below is sufficient to obtain optimal benefits without causing any harm to the body. According to methodological recommendations MP 2.3.1.2432-08 dated December 18, 2008, the following consumption standards have been established in Russia:
For children
General characteristics of vitamin B4 (Choline)
Vitamin B4 in its pure form was obtained in the 19th century from bile, but its role for humans became known in 1930, after a series of experiments on animals.
Choline (from Greek χολή - bile) is a vitamin-like substance that has membrane-protective (protects cell membranes from destruction and damage), anti-atherosclerotic (reduces cholesterol levels in the blood), nootropic, antidepressant, and calming effects. Choline improves metabolism in nervous tissue, prevents the formation of gallstones, normalizes fat metabolism and helps reduce weight.
Choline, its salts and esters are registered as a food additive.
Physico-chemical properties of vitamin B4
Vitamin B4 is a hygroscopic, colorless crystal, highly soluble in water, and is destroyed by heat treatment.
Choline can be synthesized independently in the body, but in environmental conditions this amount is not enough, so doctors recommend increasing its content in the body with food.
The richest product in choline is. Good sources of B4 are: liver, kidneys, meat, fish, cottage cheese, cheese. , legumes, some vegetables (,) also contain choline.

Daily requirement of vitamin B4
Vitamin B4 is especially necessary for people engaged in mental work, schoolchildren, students, as well as people engaged in heavy physical labor, and athletes.
Daily requirement for choline:
- Children from 0 to 11 months - 50-70 mg;
- Children from 1 year to 3 years - 70-90 mg;
- Children from 3 to 7 years old - 100-200 mg;
- Children from 7 to 18 years old - 200-500 mg;
- Men and women over 18 years of age is 500 mg;
- Pregnant women - 700 mg;
Choline plays a large role in the normal functioning of the nervous system. It is involved in the formation of the protective myelin sheath of nerves (calorizator). The presence of choline in the body protects against the destruction of the myelin layer and damage to nerve cells. Choline is also an essential component of cell phospholipids (membranes).
Choline is a precursor to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, the most important neurotransmitter and transmitter of nerve impulses. Thus, choline prevents nervous system disorders.
Choline is also a hepatoprotector, accelerating the structural restoration of damaged liver tissue due to the toxic effects of drugs, viruses, alcohol and drugs. It improves liver function and prevents the formation of gallstones.
Choline reduces cholesterol levels and the concentration of fatty acids in the blood, clears the walls of blood vessels from cholesterol plaques. Choline promotes the formation of methionine, which removes excesses of a special substance - homocysteine, which increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. As a result, choline strengthens the heart muscle and normalizes heart rhythm.
In the pancreas, vitamin B4 is involved in carbohydrate metabolism. It strengthens the membranes of beta cells that produce insulin, thus normalizing blood sugar levels. In type I diabetes mellitus, choline consumption helps reduce the need for insulin. In type II diabetes mellitus, choline helps compensate for the lack of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the body in order to reduce excess insulin levels (excess insulin is one of the factors in the development of type II diabetes mellitus).
Choline plays an important role in human reproduction. It is involved in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins in the prostate gland, increases sperm motility, and prevents disruption of the prostate gland in old age.
Choline stimulates the enzymatic breakdown of fats, normalizing fat metabolism.

At the end of the eighties of the last century, an experiment was conducted: English psychophysiologists gave 10 grams of choline to a group of volunteers for 10 days (calorizer). Tests conducted at the beginning and end of the experiment showed a significant improvement in the subjects' short-term memory.
Choline is the most important building material of the brain. Additional consumption of it by pregnant women (the fetus cannot produce it on its own) and by children in the first five years of life has a positive effect on the mental abilities of children.
Harmful properties of vitamin B4
Vitamin B4 can only cause harm if it is overdosed. May cause: hypersensitivity, nausea, increased salivation and sweating, intestinal upset.
Vitamin B4 absorption
Indicators of choline deficiency (hypovitaminosis) in the body are:
- irritability, nervous breakdowns, fatigue;
- diarrhea (when eating fatty foods), gastritis;
- deterioration of liver and kidney function;
- high blood pressure;
- growth slowdown;
- headache;
- noise in ears;
- arrhythmia.
Excess vitamin B4 in the body
Usually, a long-term excess of vitamin B4 in the body does not cause painful effects. But in some individual cases, the following symptoms may appear: nausea, increased sweating, intestinal upset, low blood pressure.